Coronavirus (COVID-19): modelling the epidemic (issue no.105)
Latest findings in modelling the COVID-19 epidemic in Scotland, both in terms of the spread of the disease through the population (epidemiological modelling) and of the demands it will place on the system, for example in terms of health care requirement.
Coronavirus (Covid-19): modelling the epidemic in Scotland (Issue No. 105)
Background
This is a report on the Scottish Government modelling of the spread and level of Covid-19 in Scotland. This updates the previous publication on modelling of Covid-19 in Scotland published on 21st July 2022. The estimates in this document provide an overview of the situation regarding the virus and help the Scottish Government, the health service and the wider public sector plan ahead.
Key Points
- The reproduction rate R in Scotland is currently estimated as being between 0.8 and 1.0, as at 19th July. Both the lower and upper limits have decreased since the last publication.
- The daily growth rate for Scotland is currently estimated as between ‑5% and -1% as at 19th July. The lower and upper limits have decreased since last publication.
- The number of new daily infections for Scotland is estimated as being between 284 and 693 per 100,000 people as at 19th July.
- Average contacts from the most recent wave of the Scottish Contact Survey (21st July - 27th July) indicate an average of 4.0 contacts. This has remained at a similar level compared to the previous wave of the survey (7th July - 13th July).
- Mean contacts within the work setting have decreased by 12% over the last two weeks whereas contacts within the other setting (contacts outside home, school and work) have increased by 15%. Contacts within the home have remained at a similar level over the same period.
- Average contacts have increased in the 18-29, 40-49 and 60-69 age groups while all remaining age groups reported a decrease in contacts.
- The biggest reduction in interactions is observed between those within the 30-39 age group with each other.
- The biggest increases in the proportion of participants visiting different locations are seen in those using public transport, increasing from 29% to 34% and individuals visiting another's home, increasing from 52% to 55%.
- The percentage of people wearing a face covering where they have at least one contact outside of the home has increased from 30% to 32%.
- 36% of people had taken at least one lateral flow test in the previous 7 days, decreasing from 46% in the previous wave of the survey pertaining to the 7th July - 13th July.
- The SPI-M-O consensus view is that by 13th September, daily hospitalisations from Covid-19 in Scotland are estimated to be between 18 and 122, and hospital occupancy is estimated to be between 276 and 1151.
- Analysis by the Edinburgh University Roslin Institute indicates that there remains a substantial variation in geographical risk of infection when considering the average recorded census age and booster vaccination uptake.
- The data show a recent decline in reported tests across all deprivation deciles, as well as a decline in reported positive tests and overall positivity. There is no clear trend in positivity with respect to deprivation. The volume of PCR testing remains very low.
- The distribution of lateral flow/LFD tests being reported continues to vary substantially by both age and deprivation status, with many fewer tests reported in younger adults across all deciles of deprivation, and for children in more deprived deciles. The high level of LFD positivity in the latter category is marked, and when compared to the high number of positives amongst the least deprived, consistent with under ascertainment being concentrated (and in turn higher circulation than the cases data suggest) in particular groups.
- Nationwide, during the period 21st July – 28th July Covid-19 wastewater (WW) levels varied between 70 to 120 million gene copies per person per day (Mgc/p/d). Considerable uncertainty is present, but indications are that in the most recent week of data, Covid-19 viral levels in WW are decreasing.
Overview of Scottish Government Modelling
Modelling outputs are provided here on the current epidemic in Scotland as a whole, based on a range of methods. Because it takes a little over three weeks on average for a person who catches SARS-CoV-2 (the causative agent of Covid-19) to show symptoms, become sick and either die or recover, there is a time lag in what our model can tell us about any changes in the epidemic.
The Scottish Government presents outputs from two models (Epidemia and Covasim) to the Epidemiology Modelling Review Group (EMRG), both using wastewater-derived data. These outputs are included in Figure 1.
The R value and growth rates are also estimated by several independent modelling groups based in universities and the UKHSA. Estimates are considered, discussed and combined at the EMRG, which sits within UKHSA. These are based on data up to 1st August.
The consensus view of the UKHSA across these methods was that the value of R in Scotland is between 0.8 and 1.0 as of 19th July 2022 (Figure 1). The lower and upper limits have both decreased since previous publication. R is an indicator that lags by two to three weeks.

Source: EMRG
The consensus from UKHSA is that the growth rate in Scotland is between -5% and -1% per day as at 19th July. The lower and upper limits have both decreased since last publication.
The various groups which report to EMRG use different sources of data in their models to produce estimates of incidence (Figure 2). The consensus view of the UKHSA across these methods, as at 19th July, was that the incidence of new daily infections in Scotland was between 284 and 693 new infections per 100,000. This equates to between 15,500 and 37,900 people becoming infected each day in Scotland.

Source: EMRG
What we know about how people's contact patterns have changed
Average contacts from the most recent wave of the Scottish Contact Survey (21st July - 27th July) indicate an average of 4.0 contacts. This has remained at a comparable level to the previous wave of the survey (7th July - 13th July) where average contacts were 4.0, as seen in Figure 3.
Mean contacts within the work setting have decreased by 12% over the last two weeks whereas contacts within the other setting (contacts outside home, school and work) have increased by 15%. Contacts within the home have remained at a similar level over the same period.

Figure 4 shows how contacts change across age group and setting. Average contacts have increased in the 18-29, 40-49 and 60-69 age groups while all remaining age groups reported a decrease in contacts.

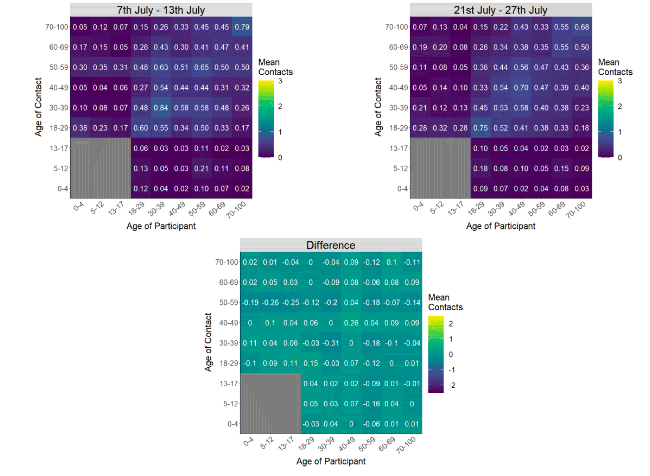
The heatmaps in Figure 5 show the mean overall contacts between age groups for the surveys relating to 7th July - 13th July and 21st July - 27th July and the difference between these periods. The biggest reduction in interactions is observed between those within the 30-39 age group with each other.
The biggest increases in the proportion of participants visiting different locations are seen in those using public transport, increasing from 29% to 34% and individuals visiting another's home, increasing from 52% to 55% as shown in Figure 6.

Figure 7 shows the percentage of people wearing a face covering where they have at least one contact outside of the home. This has increased from 30% to 32% since the last wave of the survey.
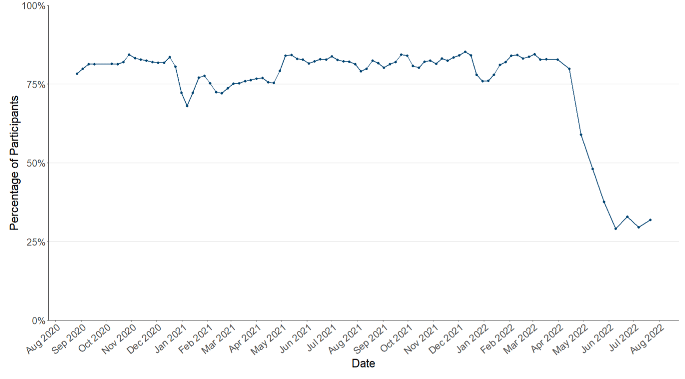
In the survey pertaining to 21st July - 27th July, 36% of people had taken at least one lateral flow test in the previous 7 days, decreasing from 46% in the previous wave of the survey pertaining to the 7th July - 13th July.

What the modelling tells us about projections of hospitalisations and hospital occupancy in the medium term
SPI-M-O produces projections of the epidemic (Figures 9 - 10), combining estimates from several independent models. These projections are not forecasts or predictions. They represent a scenario in which the trajectory of the epidemic continues to follow the trends that were seen in the data available to 1st August and do not include the effects of any future policy or behavioural changes. The delay between infection, developing symptoms and the need for hospital care means they cannot fully reflect the impact of behaviour changes in the two to three weeks prior to 1st August. The projections include the potential impact of vaccinations over the next few weeks. Modelling groups have used their expert judgement and evidence from UKHSA, Scottish Universities & Public Health Scotland, and other published efficacy studies when making assumptions about vaccine effectiveness

Figure 10 shows the SPI-M-O consensus on hospital occupancy. Hospital occupancy is determined by the combination of admissions and length of stay, the latter of which is difficult to model with confidence.

The SPI-M-O consensus view is that by 13th September, daily hospitalisations from Covid-19 in Scotland are estimated to be between 18 and 122, and hospital occupancy is estimated to be between 276 and 1,151.
Summary of spatial analysis of Covid-19 spread in Scotland
Researchers at the Edinburgh Roslin Institute have conducted spatial analysis of COVID-19 Spread in Scotland. A summary of findings from data up to 28th July 2022 is included here.
Rates of LFD and PCR testing continue to decline.
The distribution of lateral flow/LFD tests being reported varies substantially by both age and deprivation status, with many fewer tests reported in younger adults across all deciles of deprivation, and for children in more deprived deciles. The high level of LFD positivity in the latter category is marked, and when compared to the high number of positives amongst the least deprived, suggests that ascertainment may be lower in younger people in deprived areas.


What can analysis of wastewater samples tell us about local outbreaks of Covid-19 infection?
Levels of Covid-19 RNA in wastewater (WW) collected at a number of sites around Scotland are adjusted for population and local changes in intake flow rate (or ammonia levels where flow is not available). See Technical Annex in Issue 34 of Scottish Government Research Findings for the methodology. These reports are based on the most recent data available. Future updates to data may lead to small retrospective changes.
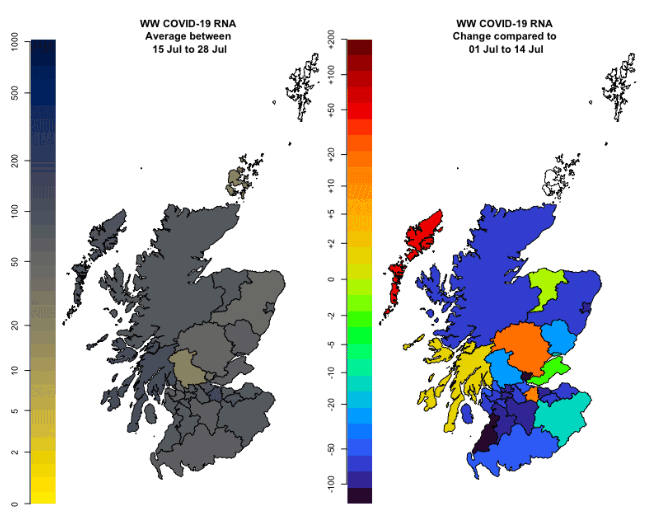
Nationwide, during the period 15th July – 28th July, Wastewater Covid-19 levels declined from around 120 to 70 million gene copies per person per day (Mgc/p/d). We conclude that these data indicate declining levels of Covid-19.
In Figure 13, we superimposed the ONS Coronavirus Infection Survey (CIS) estimate, with the newest results being up until the 20th of July. The CIS estimate seems to support a decline in Covid-19 prevalence. Note that the ONS survey has stopped publishing data on sub-regional level from July on due to a transition to a new digital data collection method. For this reason, we cannot provide comparisons to the CIS data on this level at the moment.

Figure 14 shows wastewater viral levels declining in period of 15th to 28th of July, with some local exceptions (notably in Na h-Eileanan Siar (the Western Isles)). As shown in Table 1 there was zero coverage in Orkney and Shetland Islands during this period.
Looking to the future
What may happen in the future around SARS-CoV-2 is uncertain and therefore there are a number of possible Covid-19 futures that may occur in the future. For example, the current Omicron wave may dissipate leaving low levels of Covid-19, or a new variant may emerge potentially having vaccine escape or increased severity, or people's behaviours may change. One approach to this uncertainty is to model alternative versions of the future through the development of different Covid-19 scenarios.
Given what we know about Covid-19 these possible futures range from a world where immunity reduces Covid-19 hospitalisations and ICU to low levels, through to variant world where a variant with immune escape enters Scotland and Covid-19 hospitalisations and ICU could increase. In between these two extremes there could be possible futures where people's behaviour becomes polarised between those who continue with Covid-19 precautions e.g. hand washing etc. and those who do.
The scenarios we provide in the next section look at what could happen for planning purposes, not to forecast what will happen. The assumptions are based on our most up to date knowledge, but do not include the effect of future changes in treatment of Covid-19 e.g. widespread use of antivirals or changes in behaviour in response to high levels of infections e.g. in variant world. Therefore, in the most extreme scenarios the peak may be lower than suggested if behaviour or restrictions changed.
There is no linear progression between the worlds and all are plausible. Each world inherently contains a different threat level requiring a different approach to management.
Immune World
In this possible future vaccines and natural immunity are effective at keeping Covid-19 at low levels. New variants may emerge in Scotland but for the foreseeable future infections are based around Omicron.
Infections may decrease from current levels over the coming weeks and months to very low levels. Likewise hospital and ICU occupancy may follow this trend relieving the pressure on healthcare services. Issues with new variants are not considered in this world and therefore levels of infections remain low.

In Immune world Covid-19 in Scotland reduces below epidemic levels, becoming endemic. Cases of Covid-19 therefore spring up only as rare outbreaks which are controlled through public health measures. People's lives return to something close to normality e.g. physical distancing is not needed but people still choose to self-isolate and hygiene is good. As vaccines are effective, take-up of first/second/third doses are good and boosters become part of an annual cycle like flu. The numbers of people who need medical treatment or hospitalisation for Covid-19 remain low.
The focus moves away from Covid-19 response and into recovery. This includes addressing learning losses, treating Long Covid and working through the hospital backlog. Wellbeing measures improve with reduced anxiety and increased happiness. Those from the highest risk groups feel they can reintegrate without government interventions. The economy begins to recover from the effects of Covid-19. Travellers do not face significant issues with trips overseas.
Polarised world
In this world, vaccines and natural immunity are effective at reducing infections. The approach followed relies on individual risk assessment and behaviours. However, society becomes polarised as some continue to take up vaccines and follow guidance while others are more reluctant. Covid-19 becomes a disease associated with those who do not or cannot get full vaccine benefit and do not or cannot adopt a risk based approach maintaining baseline measures.
Impacts on hospital/ICU occupancy are uncertain but levels may be higher than has been observed in summer 2020 and 2021 and higher than what may happen in Immune world (see Figure 16).

Cases of Covid-19 spring up and are hard to control in those who are not vaccinated or vulnerable. People's lives return to a "new normal" but, due to polarised groups in society with some following and some not following guidance, infections remain.
Vaccines are effective so older and more vulnerable people come forward for future doses in high numbers.
The focus remains on Covid-19 and the shift onto recovery is slower. Existing learning losses are harder to rectify and continue to accrue due to infections within education settings. The hospital backlog is difficult to address as hospitals are still dealing with Covid-19 cases. The population becomes polarised in to those whose wellbeing improves e.g. lower risk people and those whose wellbeing deteriorates e.g. higher risk or poorer people whose levels of anxiety increase as Covid-19 circulates. They continue to experience greater illness, greater poverty or disruption to their income. The economy continues to be impacted from the effects of Covid-19.
Variant world – vaccine escape with same severity as Delta
In this possible future a variant with vaccine escape emerges in Scotland presenting a challenge even for fully vaccinated people. This new variant leads to increased transmission, but not to increased severity compared to previous variants. In this scenario other NPIs may need to be put in place for a short time. This world is similar to what has happened in Scotland with the emergence of Omicron.
Omicron may be reduced to low levels within Scotland as a new variant takes over. This causes a new wave of Covid-19 infections as well as increases in hospital and ICU occupancy. People's lives are disrupted due to the increasingly high levels of infections leading to time off work ill or isolating.
To show the potential impact assume a new variant appears in Scotland as people return from their summer holidays and return to work and school. The timing is uncertain and a potential new variant may appear sooner than the summer or significantly later but has currently been lined up with the summer holidays to show illustratively what could happen. The new variant may cause Omicron infections to decrease significantly or disappear entirely (and is not shown). The new variant is modelled with similar transmissibility and vaccine escape as Omicron with severity characteristics similar to Delta. It could lead to high levels of infections leading to hospital occupancy rising above capacity restrictions. With sustained high levels of infection we could again see increased staff absences in a number of sectors that were affected by this in the recent Omicron wave.

The focus remains on Covid-19 and it is hard to shift on to recovery. Continued infections within education settings and staff shortages may impact schools. The Covid-19 strain on hospitals is high due to the very high numbers of infections and workforce pressures grow making it difficult to address the hospital backlog. Wellbeing measures deteriorate with people reporting low happiness and general 'tiredness with it all'. The economy continues to be impacted from the effects of Covid-19 with many people off work. Travellers may not want to come to the UK as the new variant sweeps through.
Variant world – vaccine escape with increased severity compared to Delta
As with the other example of Variant world, a new variant appears in Scotland as people return from their summer holidays and return to work and school. The timing is uncertain but has currently been lined up with the summer holidays where reduced travel restrictions may make it more likely that a new variant is brought into Scotland.
The new variant may cause Omicron infections to decrease significantly or disappear entirely (and this is not shown on the graph). It is modelled with similar transmissibility and vaccine escape as Omicron with severity characteristics 50% higher than Delta, purely for illustrative purposes.
It could lead to high levels of infections leading to hospital occupancy rising significantly. With sustained high levels of infection we could again see increased staff absences in a number of sectors that were affected by this in the recent Omicron wave.

The focus remains on Covid-19 and it is hard to shift on to recovery. Continued infections within education settings and staff shortages may impact schools. The Covid-19 strain on hospitals is high due to the very high numbers of infections and workforce pressures grow making it difficult to address the hospital backlog. Wellbeing measures deteriorate with people reporting low happiness and general 'tiredness with it all'. The economy continues to be impacted from the effects of Covid-19 with many people off work. Travellers may not want to come to the UK as the new variant sweeps through.
What next?
Archiving of models is currently being undertaken via the Data Science Scotland GitHub organisation. Details of the Epidemia model has most recently been made available. More models will be added over the coming weeks - see the Technical Annex of issue 96 for further details.
Contact
There is a problem
Thanks for your feedback