Coronavirus (COVID-19): modelling the epidemic (issue no. 52)
Latest findings in modelling the COVID-19 epidemic in Scotland, both in terms of the spread of the disease through the population (epidemiological modelling) and of the demands it will place on the system, for example in terms of health care requirement.
Modelling the epidemic in Scotland (Issue No. 52)
Background
This is a report on the Scottish Government modelling of the spread and level of Covid-19. This updates the previous publication on modelling of Covid-19 in Scotland published on 13 May 2021. The estimates in this document help the Scottish Government, the health service and the wider public sector plan and put in place what is needed to keep us safe and treat people who have the virus.
This edition of the research findings focuses on the epidemic as a whole, looking at estimates of R, growth rate and incidence as well as local measures of change in the epidemic.
In Scotland, the modelled estimate for R is between 0.9 and 1.2, with the growth rate increasing to between -3% and 2% and modelled estimates of infections now plateauing or increasing over the next four weeks. Furthermore, positive test data over the last week is showing an increase in Covid-19 cases, and this is also being reflected in the wastewater data. Exceedance modelling indicates that there are nine local authority areas at higher risk of increasing transmission.
All of the measures modelled for this week, as described above, indicate that we are seeing a deteriorating position in Scotland, with considerable uncertainty as to what this means for future weeks.
Key Points
- The reproduction rate R in Scotland is currently estimated as being between 0.9 and 1.2. This is an increase in the range since last week.
- The number of new daily infections for Scotland is estimated as being between 4 and 10, per 100,000 people. This has increased since last week.
- The growth rate for Scotland is currently estimated as being between -3% and 2%. This is an increase in the top of the range since last week.
- Average contacts have increased by 12% in the last two weeks (comparing surveys pertaining to 22nd – 28th April and 6th - 12th May) with a current level of 4.3 daily contacts.
- The biggest increase in contacts is seen within leisure settings (contacts outside of the school, home and work), rising by 26%. Contacts within work and school have also increased by 14% and 22% respectively.
- All individuals with the exception of those aged between 40 and 59 increased their contacts in the last two weeks. The biggest increase is seen by those aged between 18-29, increasing by 50%, largely driven by work contacts.
- The biggest increase in interactions between age groups is seen between those aged 18-29 with each other, increasing by 170%.
- The biggest change in the proportion of participants visiting different locations is seen in those visiting a pub or restaurant. This has increased from less than 2% to 29% in the last two weeks, followed by visiting a non-essential shop, increasing from 22% to 39%, coinciding with the easing of restrictions on 26th April.
- Hospital bed and ICU occupancy are projected to plateau or rise over the next few weeks, as a result of relaxations of non-pharmaceutical interventions.
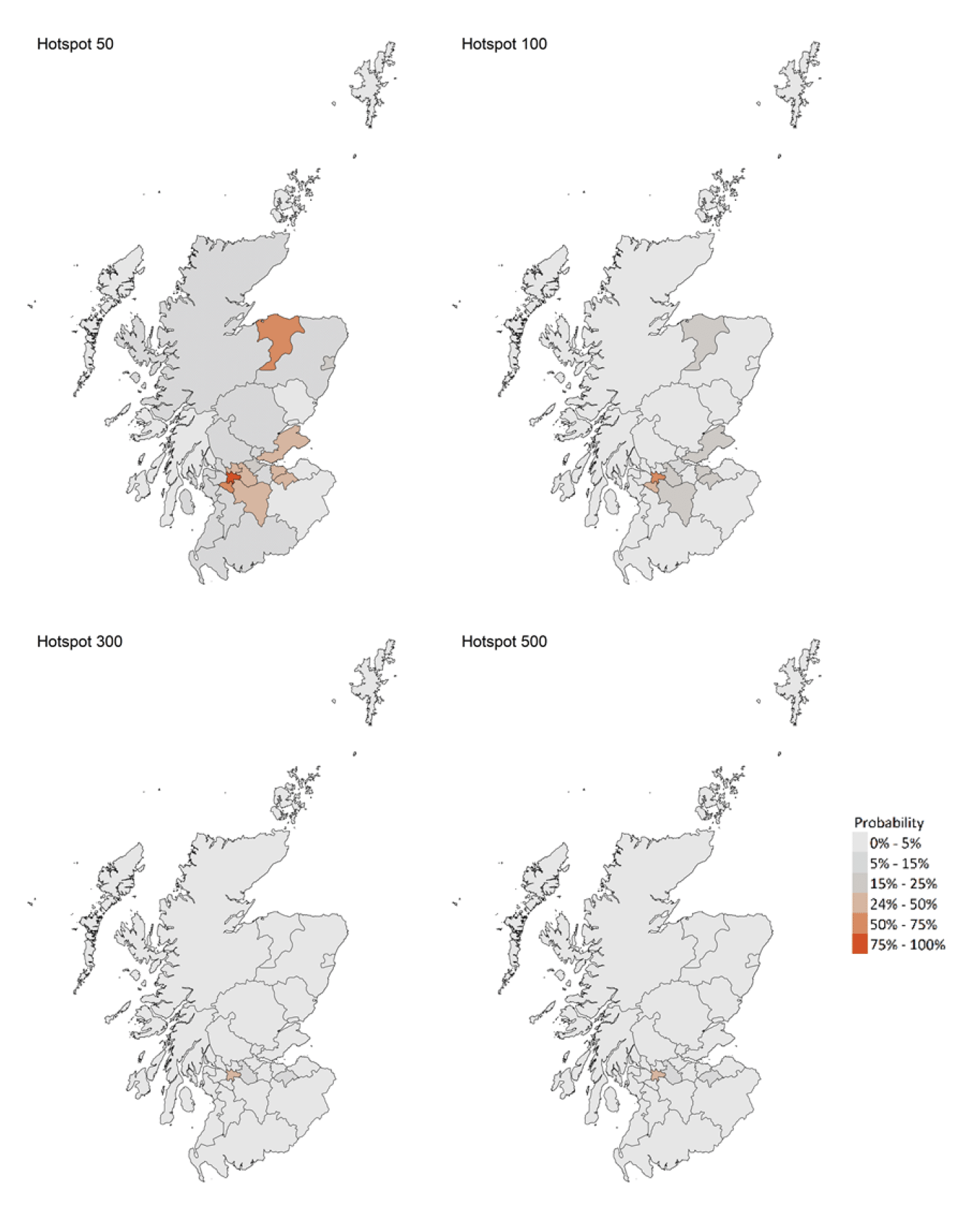
- There were nine local authority areas that exceeded what would be expected at this stage in the epidemic. Between 13th and 19th May, Midlothian, Stirling, Glasgow City, Clackmannanshire, East Dunbartonshire, East Renfrewshire, Na h-Eileanan Siar, Borders and Edinburgh were areas at higher risk of increasing transmission.
- Modelled rates per 100K indicate that for the week commencing 30 May 2021, the only local authority with at least a 75% probability of exceeding 50 cases is Glasgow City.
- The overall level of wastewater Covid-19 has increased notably this week, reaching around two and a half times last week's levels and exceeding the rate of increase in cases. This is particularly driven by new outbreaks in the Glasgow area.
- Alloa in Clackmannanshire and Lerwick in the Shetland Islands both show increases in virus levels that are not yet reflected by the case levels. Additional sites where wastewater shows a rise in Covid‑19, albeit to a lesser extent, are Hatton around Dundee, Inverclyde, Allanfearn in the Highlands, and some sites in the Falkirk area.
Overview of Scottish Government Modelling
Epidemiology is the study of how diseases spread within populations. One way we do this is using our best understanding of the way the infection is passed on and how it affects people who catch it to create mathematical simulations. Because people who catch Covid-19 have a relatively long period in which they can pass it on to others before they begin to have symptoms, and the majority of people infected with the virus will experience mild symptoms, this "epidemiological modelling" provides insights into the epidemic that cannot easily be measured through testing e.g. of those with symptoms, as it estimates the total number of new daily infections and infectious people, including those who are asymptomatic or have mild symptoms.
Modelling also allows us to make short-term forecasts of what may happen with a degree of uncertainty. These can be used in health care and other planning. The modelling in this research findings is undertaken using different types of data which going forward aims to both model the progress of the epidemic in Scotland and provide early indications of where any changes are taking place.
Modelling outputs are provided here on the current epidemic in Scotland as a whole, based on a range of methods. Because it takes a little over three weeks on average for a person who catches Covid-19 to show symptoms, become sick, and either die or recover, there is a time lag in what our model can tell us about any re-emergence of the epidemic and where in Scotland this might occur. However modelling of Covid-19 deaths is an important measure of where Scotland lies in its epidemic as a whole. In addition, the modelling groups that feed into the SAGE consensus use a range of other data along with deaths in their estimates of R and the growth rate. These outputs are provided in this research findings. The type of data used in each model to estimate R is highlighted in Figure 1.
We use the Scottish Contact Survey (SCS) to inform a modelling technique based on the number of contacts between people. Over time, a greater proportion of the population will be vaccinated. This is likely to impact contact patterns and will become a greater part of the analysis going forwards.
The delivery of the vaccination programme will offer protection against severe disease and death. The modelling includes assumptions about compliance with restrictions and vaccine take-up. Work is still ongoing to understand how many vaccinated people might still spread the virus if infected. As Covid-19 is a new disease there remain uncertainties associated with vaccine effectiveness. Furthermore, there is a risk that new variants emerge for which immunisation is less effective.
The logistical model utilises results from the epidemiological modelling, principally the number of new infections. The results are split down by age group, and the model is used to give a projection of the number of people that will go to hospital, and potentially to ICU. This will continue to be based on both what we know about how different age groups are effected by the disease and the vaccination rate for those groups.
What the modelling tells us about the epidemic as a whole
The various groups which report to the Scientific Pandemic Influenza Group on Modelling (SPI-M) use different sources of data in their models (i.e. deaths, hospital admissions, cases) so their estimates of R are also based on these different methods. SAGE's consensus view across these methods, as of 19th May, was that the value of R in Scotland was between 0.9 and 1.2 (see Figure 1). This has increased from the range of 0.8 to 1.0 last week[1].

Source: Scientific Advisory Group for Emergencies (SAGE).
The various groups which report to the Scientific Pandemic Influenza Group on Modelling (SPI-M) use different sources of data in their models to produce estimates of incidence (Figure 2). SPI-M's consensus view across these methods, as of 19th May, was that the incidence of new daily infections in Scotland was between 4 and 10 new infections per 100,000. This is an increase since last week. This equates to between 200 and 500 people becoming infected each day in Scotland.

Source: Scientific Pandemic Influenza Group on Modelling (SPI-M).
The consensus from SAGE for this week is that the growth rate in Scotland is between -3% and 2% per day. This is an increase in the top of the range from 12th May.
What we know about how people's contact patterns have changed
Average contacts have increased by approximately 12% in the last two weeks (comparing surveys pertaining to 22nd – 28th April and 6th -12th May) with a current level of 4.3 daily contacts as seen in Figure 3. The biggest increase in contacts is seen within the leisure settings (contacts outside of the school, home and work), rising by 26%. Contacts within work and school have also increased by 14% and 22% respectively. In contrast contacts within the home setting have decreased slightly (5%) over the same period.

Figure 4 shows how contacts change across age group and setting. All individuals with the exception of those aged between 40 and 59 increased their contacts in the last two weeks. The biggest increase is seen by those aged between 18-29, increasing by 50%, largely driven by work contacts. All age groups have decreased their contacts within the home, with those aged between 18-29 showing the biggest decrease in this setting (10%).

The heatmaps in Figure 5 show the mean overall contacts between age groups for the weeks relating to 22nd – 28th April and 6th - 12th May, and the difference between these periods. The biggest increase is seen between those aged 18-29 with each other, increasing by 170%. This age group has also increased interactions with all age groups 30 and over but decreased their interactions with those under 18.

The biggest change in the proportion of participants visiting different locations is seen in those visiting a pub or restaurant. This has increased from less than 2% to 29% in the last two weeks, followed by visiting a non-essential shop, increasing from 22% to 39%, coinciding with the easing of restrictions on 26th April. The proportion of individuals visiting another's home has shown a slight decrease for the first time since the middle of January, at a current level of 41%.

Vaccinations and contacts patterns
From Figure 7, it can be seen that even when contacts have increased for all age groups, cases and deaths have decreased. This coincides with the increasing number of vaccinations supplied to the population.

What the modelling tells us about estimated infections as well as Hospital and ICU bed demand
The Scottish Government assesses the impact of Covid-19 on the NHS in the next few weeks in terms of estimated number of infections. For more on how we do this see page 4 of Issue 1 of the Research Findings[4]. Figure 8 shows two projections[5], where the better projection does not account for a new variant and the worse projection does[6]. The projections also take into account the recent increase in infections observed in the last week.

Figure 9 shows the impact of the projections on the number of people in hospital. The modelling includes all hospital stays, whereas the actuals only include stays up to 28 days duration which are linked to Covid-19. Work is ongoing to show the modelled occupancy for stays up to a 28 day limit.

Figure 10 shows the impact of the projection on ICU bed demand.

A comparison of the actual data against historical projections is included in the Technical Annex.
What the modelling tells us about projections of hospitalisations and deaths in the medium term
SAGE produces projections of the epidemic[9] (Figure 11), combining estimates from several independent models (including the Scottish Government's logistics modelling, as shown in Figures 8-10). These projections are not forecasts or predictions. They represent a scenario in which the trajectory of the epidemic continues to follow the trends that were seen in the data up to 17 May.
Modelling groups have used data from contact surveys, previous findings[10] and their own expert judgement to incorporate the impact of recent relaxations on transmission. The projections do not include the effects of any other future policy or behavioural changes.
The delay between infection, developing symptoms, the need for hospital care, and death means they will not fully reflect the impact of behaviour changes in the two to three weeks prior to 17 May. Projecting forwards is difficult when the numbers of cases, admissions and deaths fall to very low levels, which can result in wider credible intervals reflecting greater uncertainty. The interquartile range can be used, with judgement, as the projection from which estimates may be derived for the next four weeks, albeit at lower confidence than the 90% credible interval.
These projections include the potential impact of vaccinations over the next four weeks. Modelling groups have used their expert judgement and evidence from Public Health England, Scottish universities, Public Health Scotland and other published studies when making assumptions about vaccine effectiveness.
Beyond two weeks, the projections become more uncertain with greater variability between individual models. This reflects the large differences that can result from fitting models to different data streams, and the influence of small deviations in estimated growth rates and current incidence.
We are not projecting the numbers of people expected to die with Covid‑19 this week. The number of daily deaths has fallen to very low levels over recent weeks. Projecting forwards is difficult when numbers fall to very low levels, therefore SPI-M-O have decided to pause producing medium term projections for daily deaths in Scotland. SPI‑M‑O's consensus view is that the number of deaths will remain very low over the next four weeks.

What the modelling tells us about whether Covid-19 infections exceeded what would be expected at this stage in the epidemic
Exceedance indicates whether the number of confirmed infections (based on testing) in each local authority area exceeds the number that was expected. Numbers of positive tests recorded each day, adjusted for population of each local authority and number of cases seen in preceding weeks, should fall within a certain distribution of values, which will rise and fall depending on the number of cases being seen nationally. Areas where the number of positive test results fall beyond the upper 95th percentile of this distribution may be at risk of seeing increased local transmission of Covid-19 and heightened vigilance may be required. This happens when the cumulative exceedance is higher than 6.0. See the Technical Annex in issue 47 for more information.
Figures 12 and 13 show exceedance for local authority areas. Recent cumulative exceedance highlights Midlothian (exceedance = 6.79), Stirling (6.66), Glasgow City (6.17), Clackmannanshire (5.53), East Dunbartonshire (5.05), East Renfrewshire (4.86), Na h-Eileanan Siar (4.75), Borders (4.00) and Edinburgh (3.29) as areas at higher risk of increasing transmission.


What we know about which local authorities are likely to experience high levels of Covid-19 in two weeks' time
We are using modelling based on Covid-19 cases and deaths from several academic groups to give us an indication of whether a local authority is likely to experience high levels of Covid-19 in the future. This has been compiled via SPI-M into a consensus. In this an area is defined as a hotspot if the two week prediction of cases (positive tests) per 100K population is predicted to exceed a threshold, e.g. 500 cases.
Modelled rates per 100K (Figure 14) indicate that for the week commencing 30 May 2021, Glasgow City was the only local authority with at least a 75% probability of exceeding 50 cases.
What can analysis of wastewater samples tell us about local outbreaks of Covid-19 infection?
Levels of Covid-19 RNA in wastewater collected at a number of sites around Scotland are adjusted for population and local changes in intake flow rate and compared to daily 7-day average positive case rates derived from Local Authority and Neighbourhood (Intermediate Zone) level aggregate data. See Technical Annex in Issue 34 of these Research Findings for the methodology.
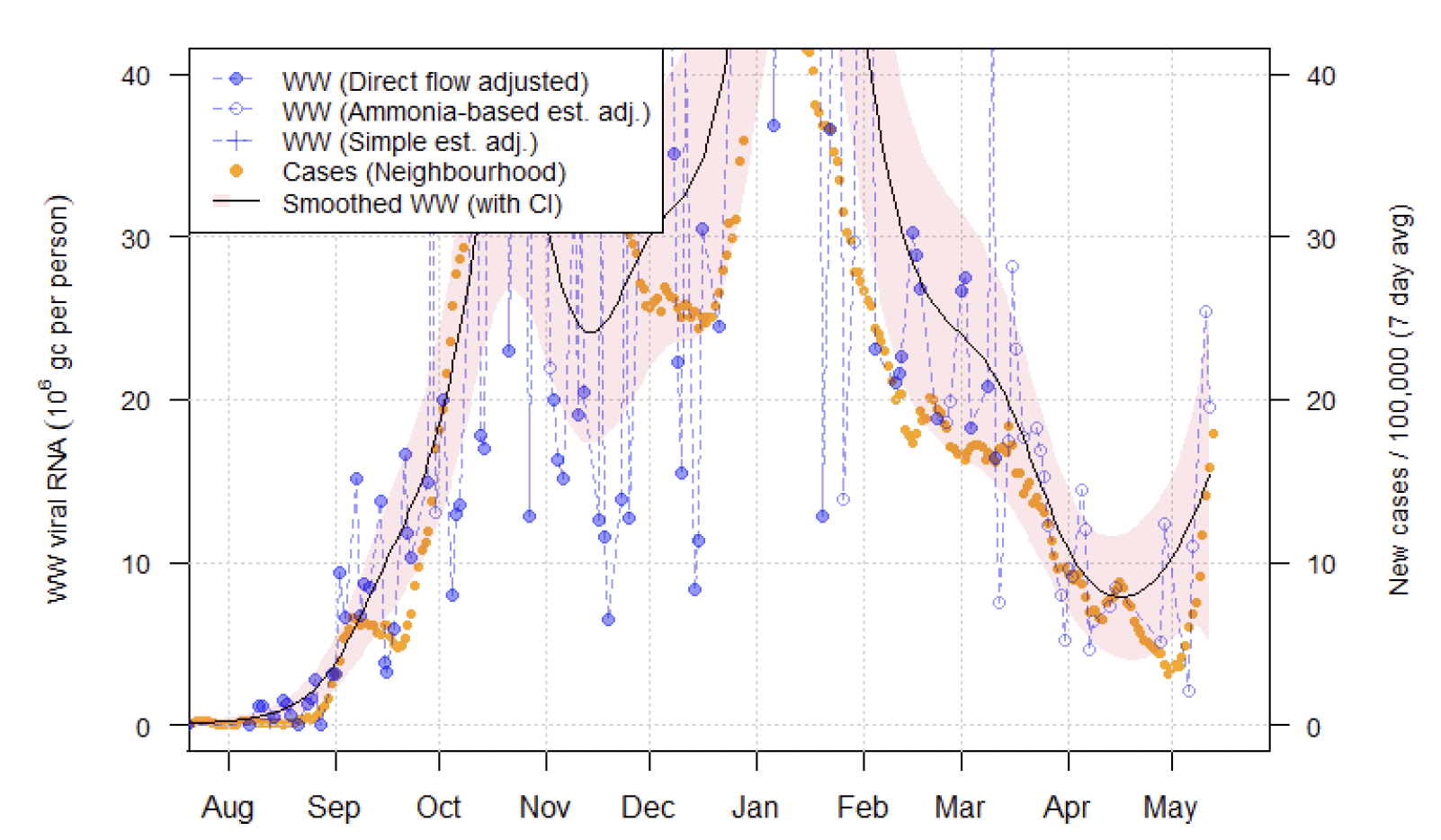
Nationwide, wastewater (WW) Covid-19 levels increased notably this week, exceeding the rate of increase in cases. This is particularly driven by new outbreaks in the Glasgow area as can be seen in the data for sites like Shieldhall, though some other locations also show an increase.
Figure 15 shows the national aggregate for the original 28 sites with long‑term records (in blue) and, from January 2021, the aggregate for the full set of up to 106 currently sampled sites (in green). This data shows a clear increase in wastewater Covid-19 levels, reaching around two and a half times last week's levels at 7.75 million gene copies per person per day (Mgc/p/d) averaged across all sites, exceeding levels seen in April.

The bulk of the rise originates from the Glasgow area. Shieldhall, a large site in this area, shows a particularly clear and large rise in recent levels of both WW Covid-19 and case rates (Figure 16). Dalmuir, also in the Glasgow area, showed a similar rise, and together these sites overlap several local authorities (Glasgow City, North and South Lanarkshire, East and West Dunbartonshire, Renfrewshire, and East Renfrewshire).
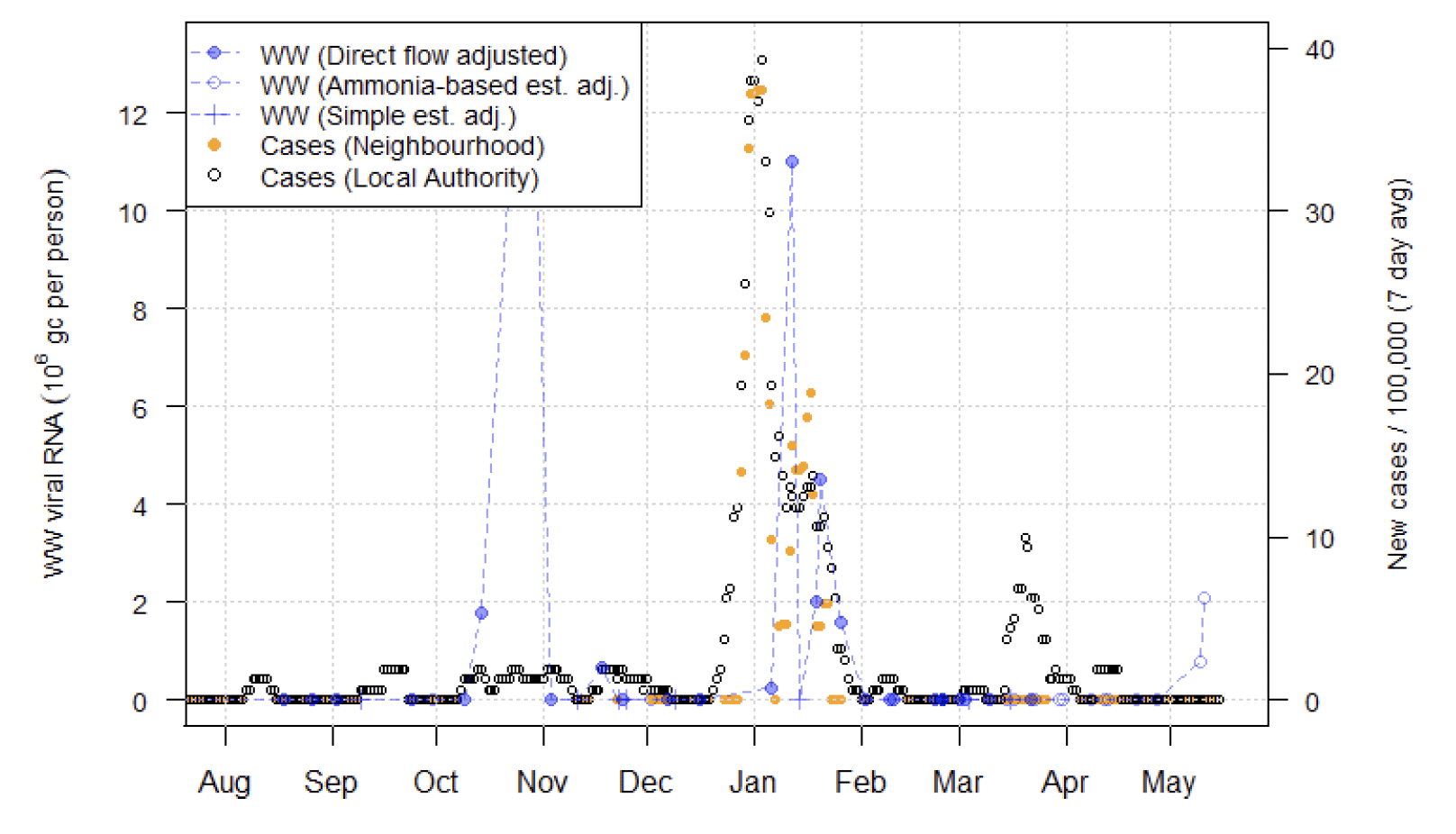
In contrast, the pattern is less clear in the Edinburgh area, where the large site at Seafield covering the City of Edinburgh and Midlothian showed no rise in WW Covid-19 levels, with similarly no increase in cases in associated neighbourhoods. However, in the Midlothian local authority there was an increase in cases, and the Penicuik wastewater site within Midlothian, remarked upon in report issue 51, continues to show high levels of the virus. However, the levels are somewhat lower in the most recent measurement than was reported on last week.
In other locations wastewater Covid-19 measurements suggest increases in virus levels that are not yet seen in the case levels. Examples include Alloa in Clackmannanshire (Figure 17) and Lerwick in the Shetland Islands (Figure 18). Both show continued elevated levels of WW Covid-19, despite no substantial rise in cases. In particular, case rates in Lerwick continue to be below the level of censoring, while consecutive WW Covid-19 measurements show a low but positive level. Additional sites where wastewater shows a rise in Covid-19 – albeit less clearly – include Hatton around Dundee, Inverclyde, Allanfearn in the Highlands, and some sites in the Falkirk area.

A more positive picture can be seen at Lossiemouth in Moray (Figure 19), where WW Covid-19 levels have declined to around 5 Mgc/p/d from the peak of over 20 Mgc/p/d, together with a decrease in case numbers of a similar magnitude.

What next?
The Scottish Government continues to work with a number of academic modelling groups to develop other estimates of the epidemic in Scotland.
The modelled estimates of the numbers of new cases and infectious people will continue to be provided as measures of the epidemic as a whole, along with measures of the current point in the epidemic such as Rt and the growth rate. Further information can be found at https://www.gov.scot/coronavirus-covid-19.
Contact
There is a problem
Thanks for your feedback