Quality prescribing for Benzodiazepines and z-drugs: guide for improvement 2024 to 2027
Benzodiazepine and z-drug prescribing continues to slowly reduce across Scotland. Despite this, benzodiazepine and z-drug prescribing remains a challenge. This guide aims to further improve the care of individuals receiving these medicines and promote a holistic approach to person-centred care.
7. Data – National Therapeutic Indicators (NTIs) and the Scottish Therapeutics Utility (STU)
National Therapeutic Indicators
To identify where your health board, GP cluster or GP practice benchmark in relation to prescribing indicators please use the following National Therapeutic Indicator dashboard. Here you will find the three-point timeline allowing you to benchmark your practice, cluster or health board region against similar areas or the Scottish average in a wide range of prescribing areas.
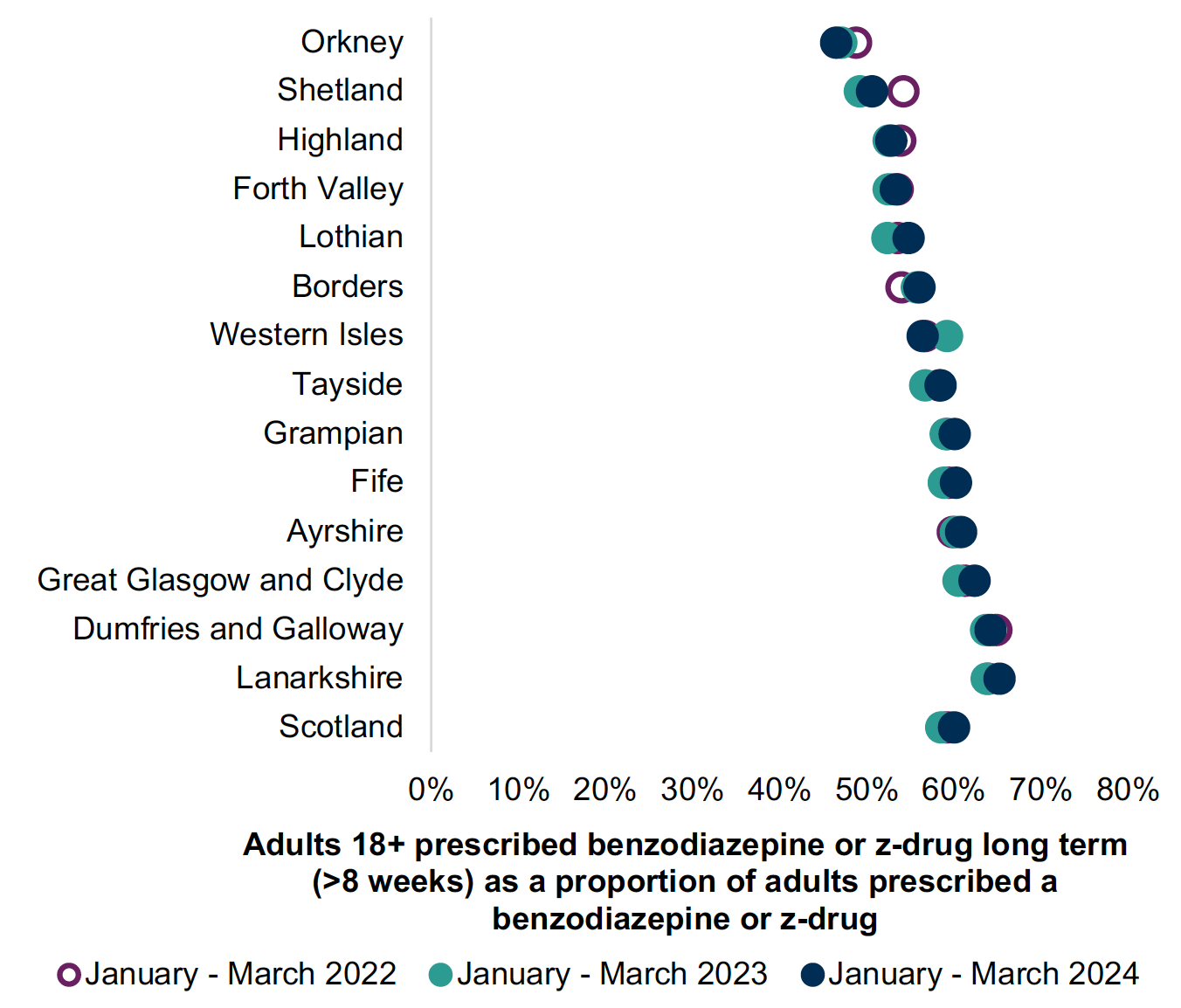
The full list of current National Therapeutic Indicators for Benzodiazepines and z-drugs are listed in Appendix 8 and a set of related searches have been developed in the Scottish Therapeutics Utility (STU) to help you identify individuals within your GP practice.
Scottish Therapeutics Utility
Once you have identified where your GP practice, GP cluster or health board sits in relation to similar clusters and the Scottish average, use the Scottish Therapeutics Utility (STU) tool in your practice to identify these individuals for review of treatment where necessary. The Scottish Therapeutics Utility tool is available to download within all general practices in Scotland and provides a suite of case finding prescribing indicators to help you identify individuals who could benefit from review. STU links to the patient record allowing you to make changes to medication within Vision and EMIS from the toolkit itself. It can be downloaded on your practice computer using the installation guide on the Effective Prescribing and Therapeutic website.
Users can click on the required prescribing indicator and select a specific patient medication record and any acute prescriptions issued in the last 84 days. Acute prescriptions are annotated with (a). The data can then be sorted by any of the columns by clicking on the column heading. As STU uses more accurate practice level data, updated in near real time, the number of patients identified in general practice may differ from the benchmarking numbers displayed on the National Therapeutic Indicators. NTIs use a different data source updated on a quarterly basis and as a result any changes made at a practice level on STU may take time to be reflected on the NTI dashboard.
Any additional STU searches that could help you or your practice in identifying issues around prescribing can be suggested to the STU team for consideration using the email nti.stu@gov.scot.
Contact
Email: EPandT@gov.scot
There is a problem
Thanks for your feedback