International Development Fund: non-communicable disease programme
This report responds to a commission by the Scottish Government to design a new international development health programme providing support to the governments of Malawi, Rwanda and Zambia with a focus on non-communicable diseases (NCDs).
Appendix 4: Country snapshots – Zambia
Economic-political situation
Despite having one of the world’s fastest growing economies in the decade prior to 2011, in 2020, 54% of the population live below the poverty line. GDP is expected to grow by 3.8% in the coming years, although there are growing inequalities in this increasingly urbanised country. Zambia is considered stable, with the last election of a new President in 2021. Zambia had been declared a lower middle-income country in 2010, and this has led to the exit of some donors, but this has since been revoked.[118]
| 2020 | 2035 | 2050 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Population (million) | 18.9 | 27.8 | 37.5 |
| Median age | 17.6 | 20.2 | 22.8 |
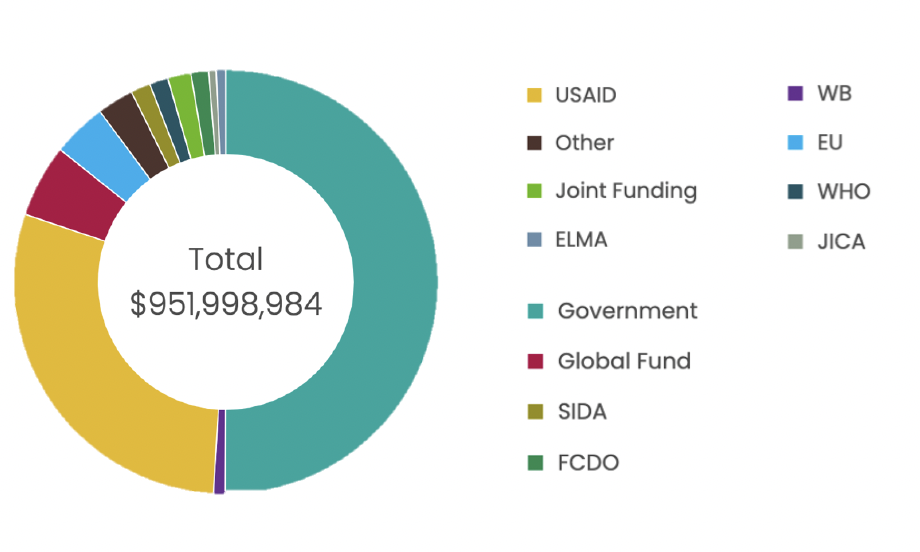
Health Funding
In 2021 government allocation to health was low, at 8.1% of the total budget. This equates to 3% of GDP. In 2022 only 15% of the health budget is expected to come from external sources. 84% of development assistance for health prioritises communicable diseases, maternal and child health, nutrition and health system strengthening. At present there are no development partners specifically on NCDs. Poor fiduciary management and corruption particularly related to medicines procurement led external partners to move away from a SWAP. However anecdotal reports suggest that recent political changes are seen as positive (KIIs). Chronic care for NCDs is not covered in insurance schemes, so OOP expenditure is high.[120]
| 2009-2010 | 2018-20 | |
|---|---|---|
| Rural population | 61.0% | 54.6% |
| Birth rate | 5.4 | 4.5 |
| Population living under national poverty line | 54.7% | 54.5% |
| Population living under international poverty line | 68.5% | 57.5% |
| GDP per capita | $1,490 | $1,121 |
| <5 mortality per 1,000 live births | 77.0 | 61.4 |
| MMR[123] per 100,000 live births | 305 | 213 |
| Life expectancy | 56 | 64 |
| Risk factor | Male | Female |
|---|---|---|
| % smokers | 24.0 | 7.8 |
| % drink alcohol | 16.8 | 5.1 |
| % obese | 3.0 | 12.3 |
| Mean salt intake | 9.5g (2 times WHO recommendation) | |

Contact
Email: socialresearch@gov.scot
There is a problem
Thanks for your feedback