Scottish seabird conservation action plan: vulnerability report
Details the process undertaken to determine the key pressures acting on seabirds whilst at Scottish seas and at breeding colonies and used to inform the development of the Scottish seabird conservation action plan.
Annex 2: Assessing Exposure
| Threat/ impact | Activity | Exposure information sources |
|---|---|---|
| Climate change | Multiple activities | Marine Climate Change Impacts Partnership (MCCIP) |
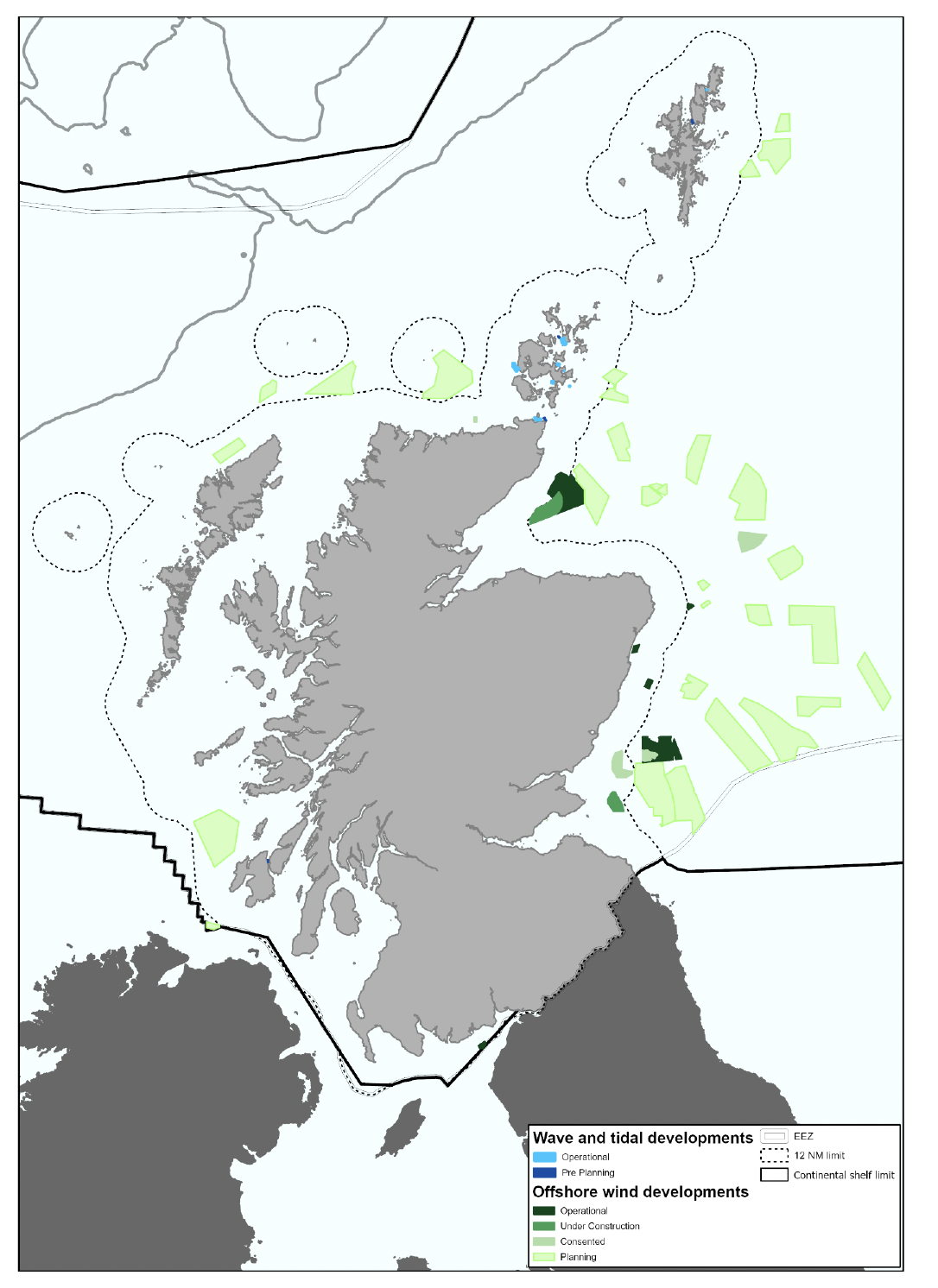
| Collision mortality, displacement and barrier to species movement. | Energy generation - Offshore wind: Operation and maintenance (Marine energy – Offshore wind) | Location of existing and planned offshore wind farms together with future planned areas for offshore wind developments identified through the Sectoral Plan for Offshore Wind Energy. |
| Underwater collision mortality | Energy generation - Tidal stream: Operation and maintenance Wave energy generation (Marine energy – wave and tidal) | Location of existing tidal developments known. (Tidal lease sites and tidal draft plan options, Marine Scotland - National Marine Plan Interactive (atkinsgeospatial.com)) |
| Marine litter | Multiple activities | Some existing marine litter indicators are available (e.g. SCRAPBook[6], OSPAR Marine indicators[7], Great British beach clean[8]). Spatial extent currently unclear, especially at scale relevant to seabirds. |
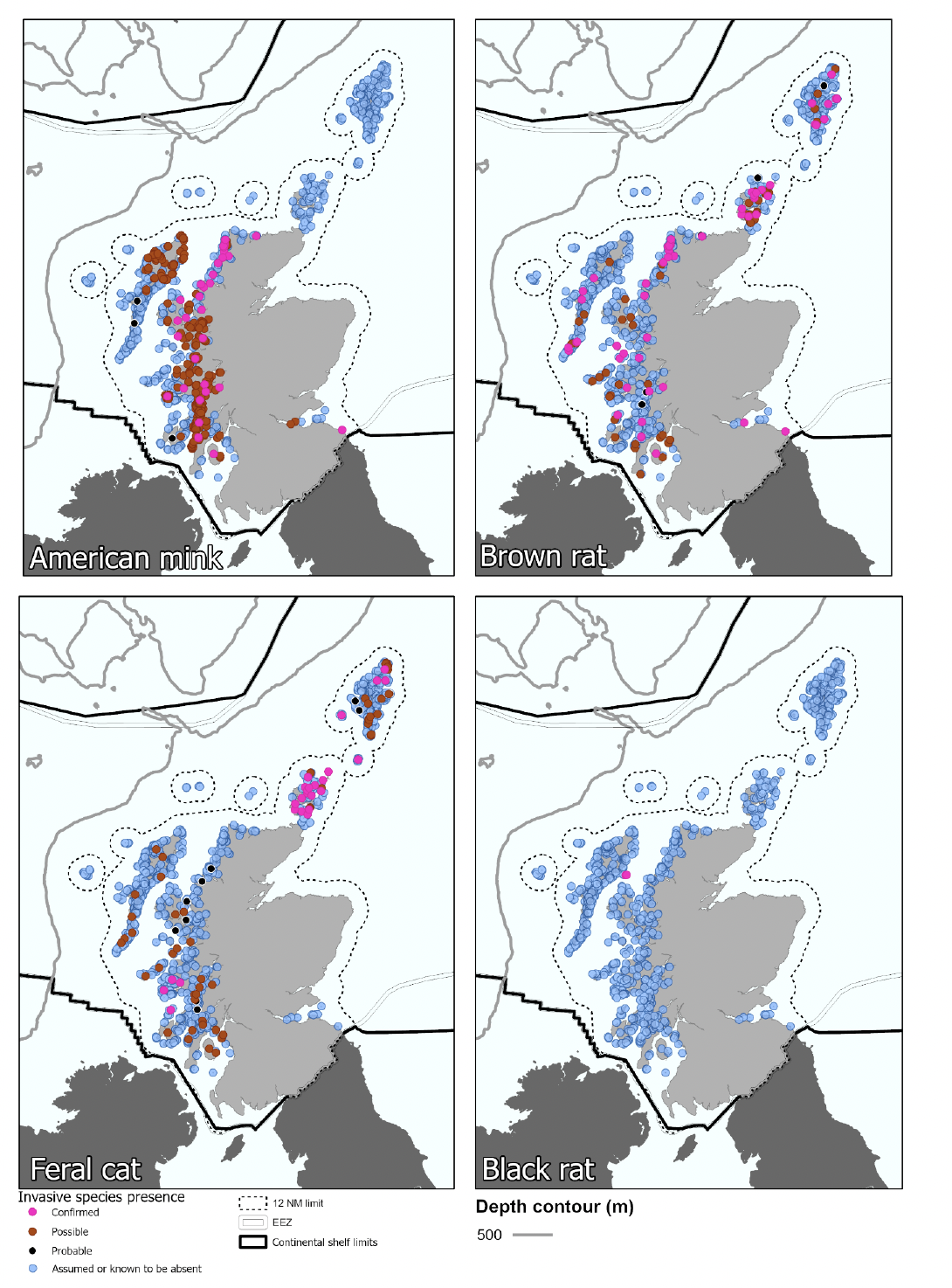
| Habitat loss & mortality from invasive predatory mammals | Multiple activities | Exposure assessments use the UK Marine Strategy assessment of invasive predatory Mammals on seabird islands (Mitchell et al. 2018) along with distribution data and maps from Stanbury et al. (2017). |
| Reduction in prey by fishing | Fisheries | ICES Advice on fishing opportunities, catch, and effort for sandeels in the North Sea. The latest advice for each sandeel area adjacent to the Scottish Coast contains information on annual fishing pressure and landings up to 2018 and estimates of stock size up to 2019. For northern North Sea & Shetland see ICES (2019a) and for northern and central North Sea see ICES (2019b). No stock assessment data available that would enable a straightforward exposure assessment for fishing pressure on other prey species – sprat, juvenile herring, juvenile cod, whiting etc. |
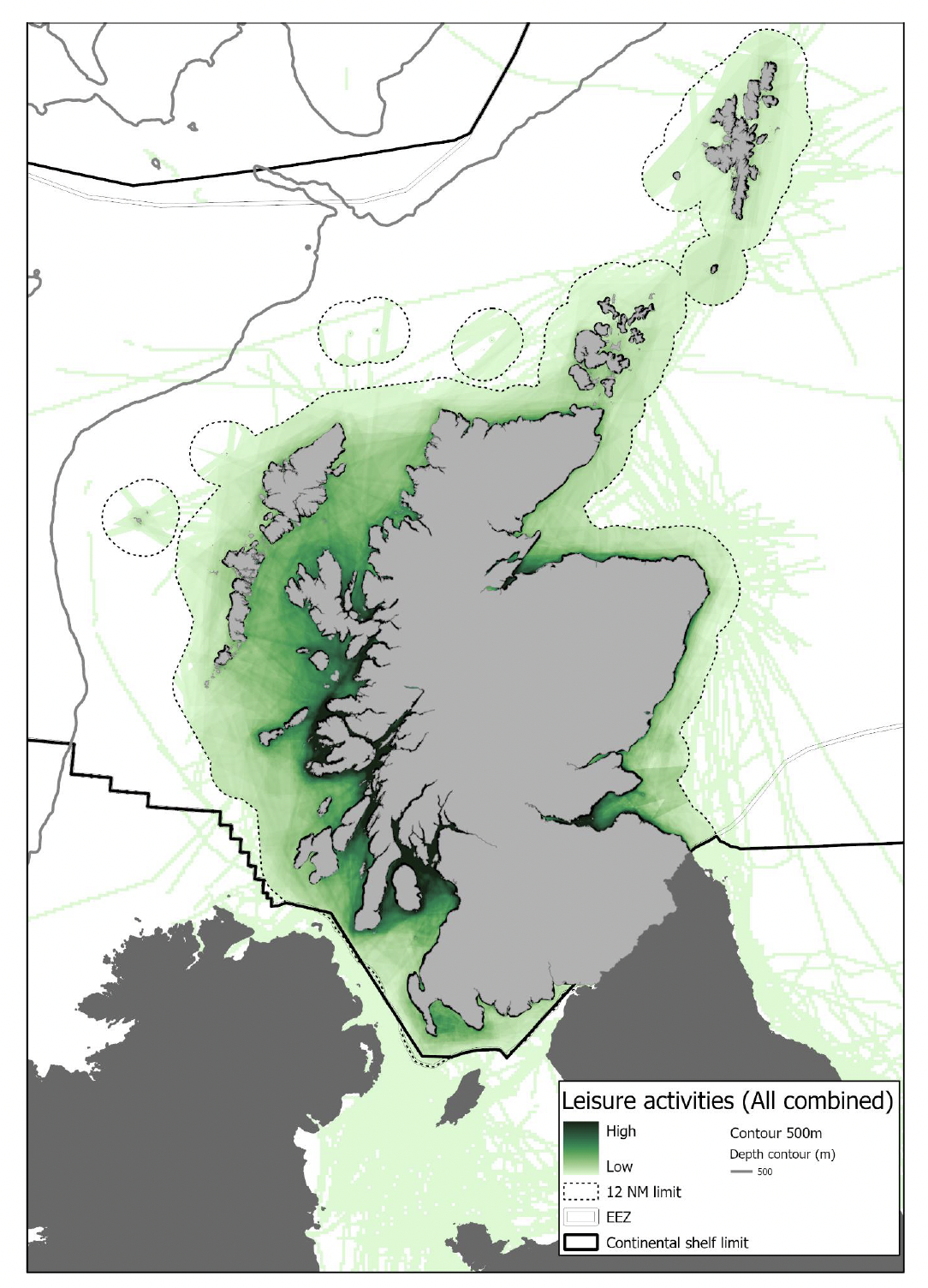
| Disturbance | Recreation, tourism and transport activities | Data on vessel traffic (available from Marine Scotland via NMPi). The distribution of a wide range of recreational activities is recorded by the Scottish Marine Recreation & Tourism Survey[9] with associated maps by activity available from Marine Scotland via NMPi. |
| Intentional taking of adults/eggs | Licenced culling, control & harvesting | NatureScot licensing data. |
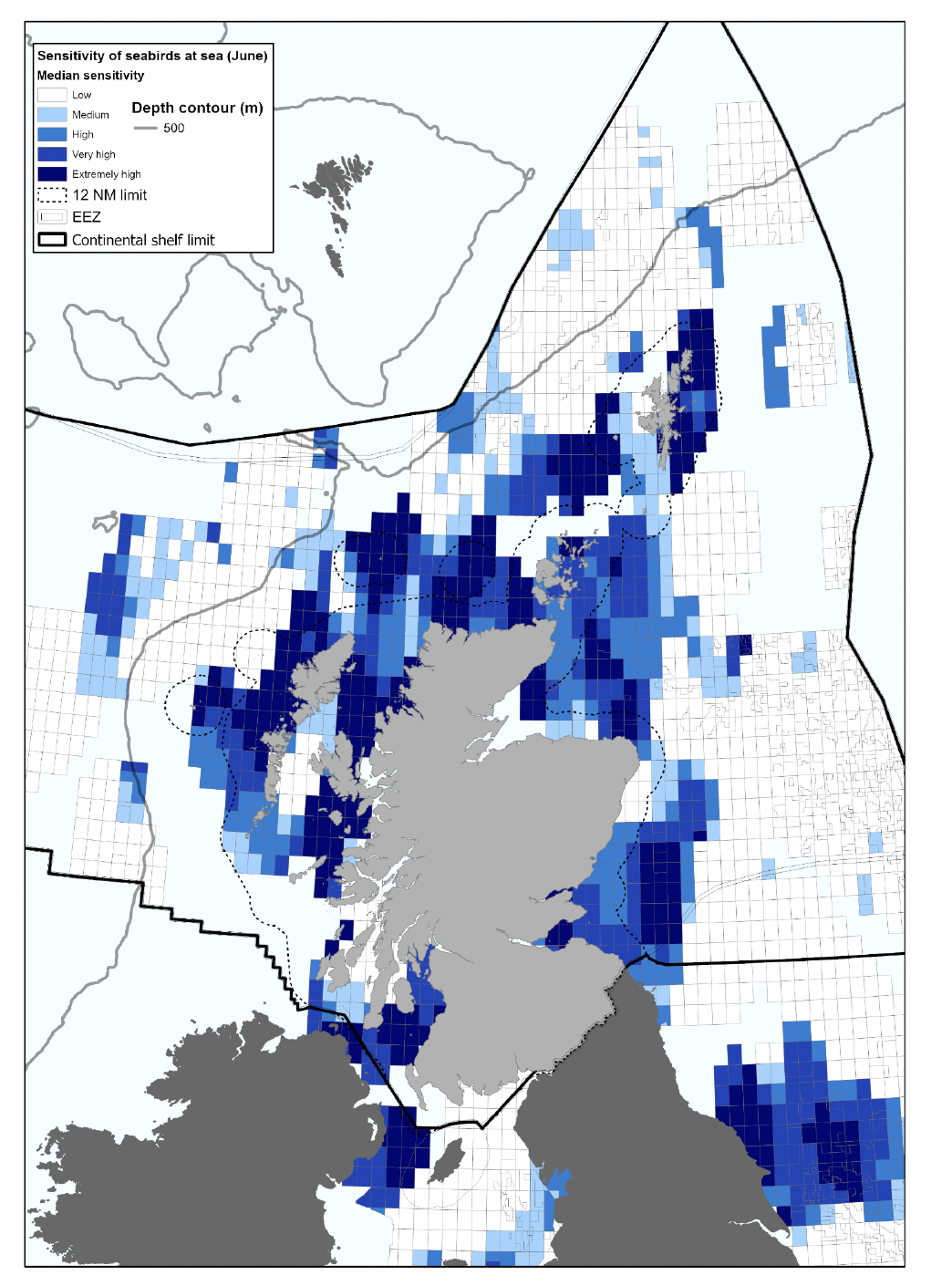
| Mortality from oil contamination | Multiple activities | Seabird Oil Sensitivity Index[10] (based upon seabird survey data collected from 1995-2015) aids planning and emergency decision making with regards to oil pollution, identifying areas at sea where seabirds are likely to be most sensitive to oil pollution. The UK Beached Bird Survey and SOTEAG[11], also undertake monitoring of oiled seabirds. |
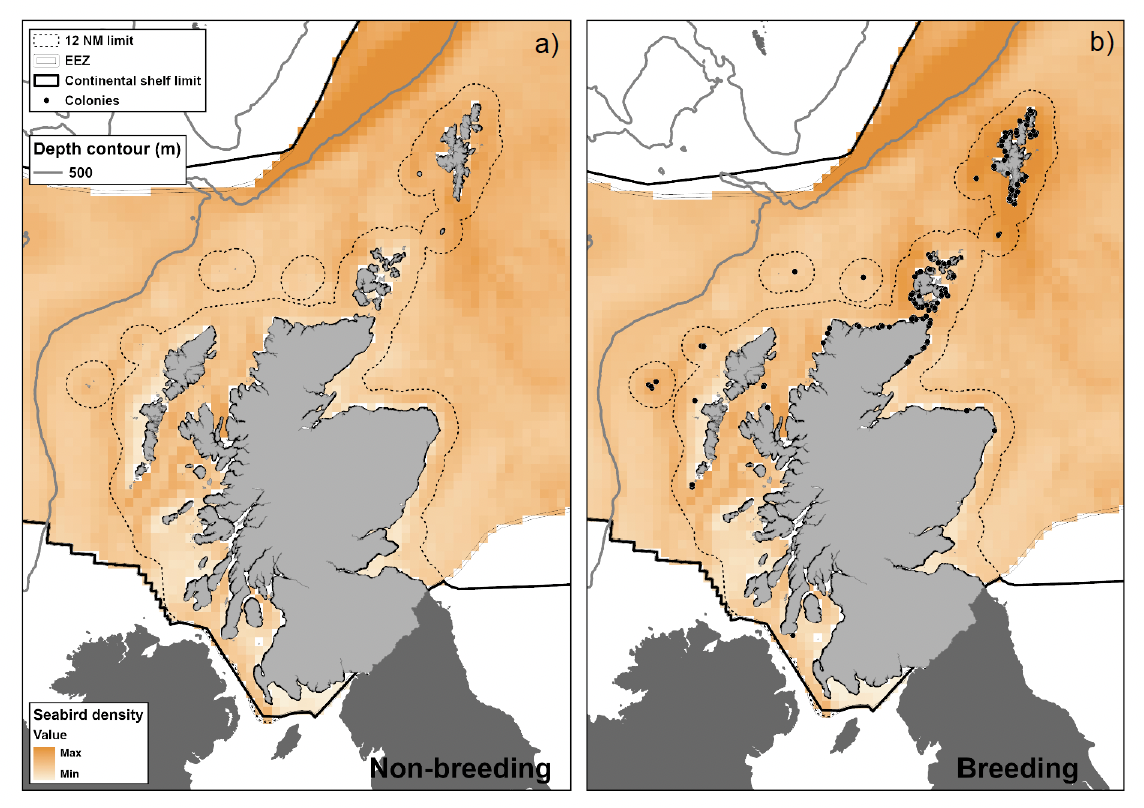
a. Northern fulmar non-breeding distribution and b. Northern fulmar breeding distribution. Offshore distribution data taken from Waggitt et al. (2019). Dots indicate colonies which contain >0.01% of the Scottish breeding population based on Seabird Monitoring Program[12] data.
| Common name | Distribution description | Distribution score | Data description | Data confidence score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Northern fulmar (Br) | Breeds throughout Scotland, but largest aggregations in North and West, and vast foraging forages throughout Scottish waters. | Widespread | Conspicuous at sea, extensive breeding survey effort and some GPS tracking data. | High |
| Northern fulmar (Nbr) | Forages throughout Scottish waters, but in lower densities than breeding. | Widespread | Conspicuous at sea, extensive survey effort and some GLS tracking data. | High |
| Manx shearwater (Br) | Breeds in a small number of sites in the West of Scotland, with extensive foraging ranges and occurs on passage elsewhere. | Localised | Relatively conspicuous at sea. One well monitored colony (Rum) but limited regular breeding survey effort elsewhere. Tracking data from a single colony in Scotland. | Medium |
| European Storm-petrel (Br) | Breeds in the West and North of Scotland, with extensive foraging ranges and occurs on passage elsewhere. | Localised | Small size makes detection at sea challenging. Limited breeding survey effort in much of range, and limited tracking data from 2 colonies. | Low |
| Leach's storm petrel (Br) | Breeds in a small number of sites in the North and West of Scotland, foraging predominantly in offshore waters in West of Scotland, although on passage elsewhere. | Localised | Relatively challenging to observe at sea with limited breeding survey effort in much of range and tracking data from 1 colony. | Low |
| Arctic skua (Br) | Breeds predominantly in the North and also West of Scotland, with foraging and passage throughout Scottish waters. | Localised | Conspicuous at sea. Due to remote/expansive breeding, limited survey effort in much of range, and limited tracking data. | Low |
| Great skua (Br) | Breeds predominantly in the North and also West of Scotland, with foraging and passage throughout Scottish waters. | Localised | Conspicuous at sea. Due to remote/expansive breeding, limited survey effort in much of range, and no tracking data due to tagging effects. | Low |
| Great skua (Nbr) | Occurs throughout Scottish waters on passage but largely absent from majority of Scotland during winter period. | Restricted | Conspicuous at sea but low densities and no tracking data. | Low |
| Great black-backed gull (Br) | Breeds throughout Scotland but greatest breeding aggregations in North and West, foraging and passage throughout Scottish waters. | Widespread | Conspicuous at sea, extensive breeding survey effort but limited GPS tracking data due to tagging effects. | Medium |
| Great black-backed gull (Nbr) | Occurs throughout Scottish waters | Widespread | Conspicuous at sea, but no tracking data. | Medium |
| Herring gull (Br) | Breeds on throughout Scotland and forages throughout Scottish waters. | Widespread | Conspicuous at sea, extensive breeding survey effort but limited tracking data in Scotland. | Medium |
| Herring gull (Nbr) | Occurs throughout Scottish waters | Widespread | Extensive survey effort but no tracking data. | Medium |
| Lesser black-backed gull (Br) | Breeds on throughout Scotland (including many terrestrial sites in the central belt) and forages throughout Scottish waters. | Widespread | Conspicuous at sea, extensive survey effort and some tracking data in Scotland. | Medium |
| Lesser black-backed gull (Nbr) | Occurs throughout Scottish waters on passage but largely absent from majority of Scotland during winter period, although some individuals remain in the South. | Restricted | Conspicuous at sea and some tracking data. | Medium |
| Little gull (Nbr) | Small numbers, predominantly in waters in South-east of Scotland. | Restricted | Limited survey effort in Scotland and no tracking data. | Low |
| Black-legged kittiwake (Br) | Breeds on throughout Scotland and forages throughout Scottish waters. | Widespread | Extensive survey effort and GPS tracking data from numerous colonies in Scotland. | High |
| Black-legged kittiwake (Nbr) | Occurs throughout Scottish waters, but lower densities than during breeding. | Widespread | Extensive survey effort and GLS tracking data from colonies in Scotland. | High |
| Little tern (Br) | Localised coastal distribution close to small number of breeding locations. Absent during non-breeding season. | Restricted | Small and challenging to detect during at sea surveys due to low densities, remote/limited breeding survey effort in Scotland and no tracking data. | Low |
| Common tern (Br) | Largely coastal distribution throughout Scotland. Absent during non-breeding season. | Localised | Conspicuous during at sea surveys, some breeding survey effort and limited tracking data in Scotland. | Medium |
| Arctic tern (Br) | Largely coastal distribution throughout Scotland. Absent during non-breeding season. | Localised | Conspicuous during at sea surveys, some breeding survey effort and limited tracking data in Scotland. | Medium |
| Sandwich tern (Br) | Largely coastal distribution throughout Scotland. Absent during non-breeding season. | Localised | Conspicuous during at sea surveys, some breeding survey effort and no tracking data in Scotland. | Medium |
| Northern gannet (Br) | Several large breeding colonies (gannetries) distributed across Scotland and forages throughout Scottish waters. | Widespread | Large and conspicuous during at sea surveys, extensive breeding survey effort and tracking data from selected colonies in Scotland. | High |
| Northern gannet (Nbr) | Occurs throughout Scottish waters, but in lower densities compared to summer and a relatively short winter period. | Widespread foraging and | Large and conspicuous during at sea surveys, and some year-round tracking data from colonies in Scotland. | High |
| Great cormorant (Br) | Largely coastal breeding distribution in the south and east of Scotland. | Localised | Conspicuous and inshore during at sea surveys, good survey effort within more coastal areas but no tracking data in Scotland. | Medium |
| Great cormorant (Nbr) | Largely coastal foraging distribution throughout Scotland. | Localised | Conspicuous and inshore during at sea surveys, and no tracking data in Scotland. | Medium |
| European shag (Br) | Coastal breeding and foraging distribution throughout Scotland. | Localised | Conspicuous and inshore during at sea surveys, good survey effort within more coastal areas, GPS tracking data from selected colonies in Scotland. | Medium |
| European shag (Nbr) | Coastal distribution throughout Scotland, with partial non-breeding migration in some populations. | Localised | Conspicuous and inshore during at sea surveys, and GLS tracking data from limited number of colonies in Scotland. | Medium |
| Razorbill (Br) | Occurs and breeds throughout Scottish waters | Widespread | Conspicuous and during at sea surveys, extensive breeding survey effort and GPS tracking data from selected colonies in Scotland. | High |
| Razorbill (Nbr) | Occurs throughout Scottish waters, but in reduced numbers and more offshore than during breeding. | Widespread | Conspicuous during at sea surveys, and GLS tracking data from colonies in Scotland. | High |
| Common guillemot (Br) | Occurs and breeds throughout Scottish waters | Widespread | Conspicuous during at sea surveys, extensive breeding survey effort and GPS tracking data from selected colonies in Scotland. | High |
| Common guillemot (Nbr) | Occurs throughout Scottish waters, but in reduced numbers and more offshore than during breeding. | Widespread | Conspicuous during at sea surveys, and GLS tracking data from colonies in Scotland. | High |
| Black guillemot (Br) | Coastal foraging and breeding distribution to the North and West of Scotland. | Localised | Conspicuous and inshore during at sea surveys, good breeding survey effort and GPS tracking data from colonies in Scotland. | Medium |
| Atlantic puffin (Br) | Occurs throughout Scottish waters. | Widespread | Conspicuous during at sea surveys, extensive breeding survey effort, but limited GPS tracking data from selected colonies in Scotland due to tagging effects. | High |
| Atlantic puffin (Nbr) | Occurs throughout Scottish waters, but in reduced numbers and more offshore than during breeding. | Widespread | Conspicuous during at sea surveys, and GLS tracking data from colonies in Scotland. | Medium |
| Pressure Name | Distribution Description | Distribution Score | Data Description | Data Confidence Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate Change | There is increasing evidence of climate change impacting seabirds throughout Scotland, both through direct impacts of extreme weather events and indirect impacts on prey populations. While the impacts vary by location, they are widespread with high exposure for all species. | Widespread | While there is high confidence that climate change is and will affect seabirds, there is low confidence as to how and where this will occur. | Low |
| Wind turbine collision mortality; displacement by wind turbines; wind turbines as barrier to species movement | Currently, several discrete wind farms are located in the seas off Eastern Scotland and within 100km of shore. However, the Sectoral Marine Plan identifies several candidate areas for future development in both the West and North. | Localised | Locations of current sites known and plans identify candidate areas for future development. | High |
| Mortality by collision with underwater turbines etc | Limited number of locations in NW of Scotland and Northern Isles. | Restricted | Locations of current sites known and plans identify candidate areas for future development. | High |
| Marine litter | Widespread, but low level exposure throughout range. | Localised | Limited information available and data collected over limited spatial/ temporal scale which may not be relevant to seabirds. | Low |
| Habitat loss & mortality from invasive predatory mammals | Majority of mainland Scotland and numerous offshore islands. Predominantly an issue during breeding and restricted to land. | Localised | Historical data for large parts of Scotland and specific surveys of other locations. Regular monitoring at some seabird colonies. | High |
| Reduction in prey by fishing | The pressure occurs throughout Scottish waters, but the spatial extent of fisheries is limited and target fish species vary regionally | Localised | Stock assessment data routinely collected. Spatial scale of assessments may not be appropriate for some seabird species/ colonies, non- commercial prey species poorly covered. | Medium |
| Disturbance from recreation, tourism and leisure and transport | Predominantly within 10km of shore. Recreational disturbance generally more limited during winter | Localised | The survey data has wide coverage but the information is not necessarily directly relevant to the threat of these activities on seabirds. Intermediate for vessel traffic (vessels <12m length not tracked). | Low |
| Intentional taking of adults/ chicks/ eggs (licenced control & harvesting) | Occurs in small numbers throughout Scotland but affects limited species. Predominantly breeding season. | Localised | Locations of legal activities known. | High |
| Mortality from oil contamination | Widespread, but low level exposure throughout range. | Medium | Long term data from beached bird surveys and surveillance by Oil and Gas sector, but more limited data on discharges from shipping traffic. | Medium |
Table A2. 4: Species for which matrix derived exposure scores were modified following expert review.
Br = breeding season, Nbr = nonbreeding season.
| Pressure Name | Exemptions | Justification |
|---|---|---|
| Wind turbine collision mortality | Northern fulmar (Br/Nbr) | Low flight heights |
| Great skua (Nbr) | Passage | |
| Lesser black-backed gull (Nbr) | Passage | |
| Little gull (Nbr) | Passage | |
| Little tern | Extreme coastal distribution | |
| Great cormorant (Br/Nbr) | Extreme coastal distribution | |
| European shag (Br/Nbr) | Extreme coastal distribution | |
| Razorbill (Br/Nbr) | Low flight heights | |
| Common guillemot (Br/Nbr) | Low flight heights | |
| Black guillemot | Low flight heights | |
| Atlantic puffin (Br/Nbr) | Low flight heights | |
| Displacement by wind turbines | Northern fulmar (Br/Nbr) | Low flight heights & extensive foraging |
| Manx shearwater | Low flight heights & extensive foraging | |
| European storm-petrel | Low flight heights & extensive foraging | |
| Leach’s storm-petrel | Low flight heights & extensive foraging | |
| Little tern | Extreme coastal distribution | |
| Great cormorant (Br/Nbr) | Extreme coastal distribution | |
| European shag (Br/Nbr) | Extreme coastal distribution | |
| Black guillemot | Extreme coastal distribution | |
| Wind turbines as a barrier to species movement | Northern fulmar (Br/Nbr) | Extensive foraging distributions |
| Manx shearwater | Extensive foraging distributions | |
| European storm-petrel | Extensive foraging distributions | |
| Leach’s storm-petrel | Extensive foraging distributions | |
| Arctic skua | Extensive foraging distributions | |
| Great skua (Br/Nbr) | Extensive foraging distributions | |
| Little tern | Extensive foraging distributions | |
| Mortality by collision with underwater turbines etc | Great cormorant (Br/Nbr) | Extreme coastal distribution |
| European shag (Br/Nbr) | Extreme coastal distribution | |
| Black guillemot | Extreme coastal distribution | |
| Habitat loss & mortality from invasive predatory mammals | Northern fulmar (Nbr) | Largely at sea |
| Great skua (Nbr) | Largely at sea | |
| Great black-backed gull (Nbr) | Largely at sea | |
| Herring gull (Nbr) | Largely at sea | |
| Lesser black-backed gull (Nbr) | Largely at sea | |
| Little gull (Nbr) | Largely at sea | |
| Black-legged kittiwake (Nbr) | Largely at sea | |
| Northern gannet (Nbr) | Largely at sea | |
| Great cormorant (Nbr) | Roosts on land throughout non-br | |
| European shag (Nbr) | Roosts on land throughout non-br | |
| Razorbill (Nbr) | Largely at sea | |
| Common guillemot (Nbr) | Largely at sea | |
| Atlantic puffin (Nbr) | Largely at sea | |
| Intentional taking of adults/chicks/ eggs (licenced control & harvesting) | Great black-backed gull (Br/Nbr) | Some licenced/unlicenced cull |
| Herring gull (Br/Nbr) | Some licenced/unlicenced cull | |
| Lesser black-backed gull (Br/Nbr) | Some licenced/unlicenced cull | |
| Northern gannet (Br) | Licenced harvest on Sula Sgeir | |
| Great cormorant (Br/Nbr) | Some licenced/unlicenced cull |
Contact
Email: marine_species@gov.scot
There is a problem
Thanks for your feedback