A Trading Nation - Realising Scotland's Hydrogen Potential: Plan for Exports
Co-produced with stakeholders in the hydrogen sector, this plan aligns with our Hydrogen Action Plan and Green Industrial Strategy. It details the steps required for Scottish businesses to grasp the export opportunities hydrogen presents, as both a commodity and in the supply chain.
2. Assurance of Demand for Hydrogen and Hydrogen Products
The scale up of production of internationally significant levels of hydrogen and hydrogen products for export will require large amounts of investment, both in production facilities and associated infrastructure for transport and storage. Critical to stimulating this growth and investment is the assurance that there is a growing global demand and market for hydrogen products.
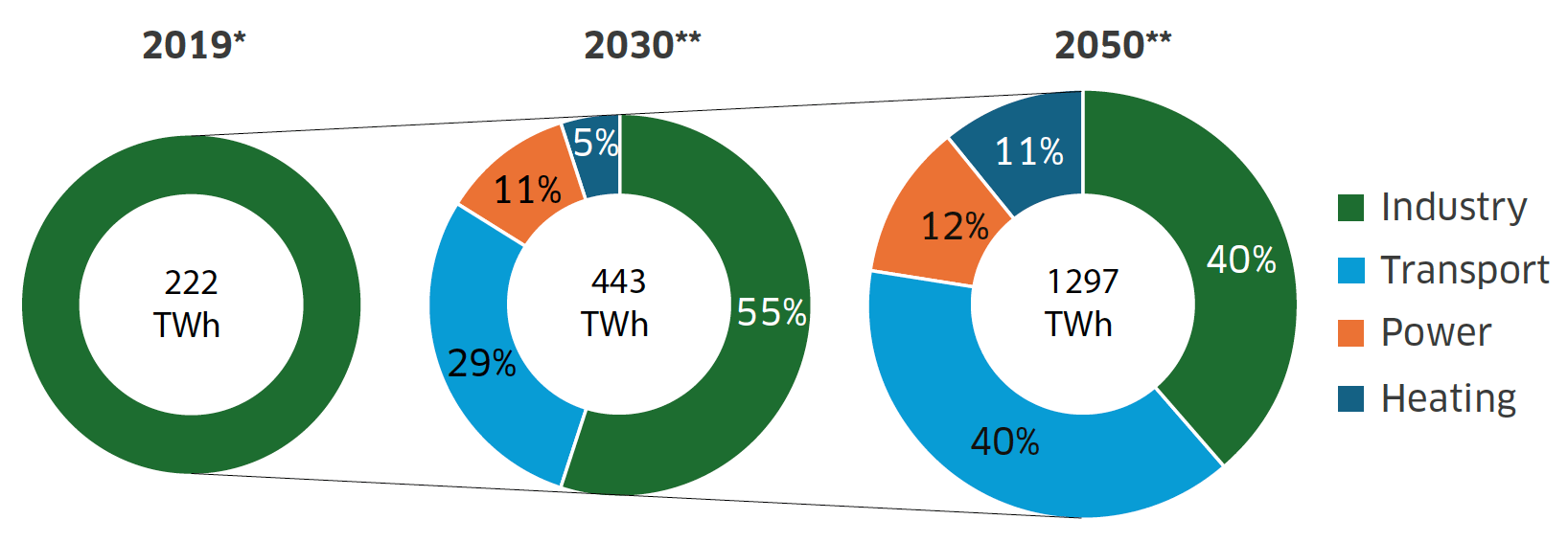
Source: Worley Consulting
* 2019 demand taken from the IEA.
** Average of demand based on scenarios from the EHB, IEA, and Aurora.
Demand in Europe for renewable and low-carbon hydrogen is widely expected to increase substantially by 2050. The European Commission is targeting 330 TWh (10 Mt) of imported hydrogen by 2030[9]. Independent analysis[10] of hydrogen demand scenarios for north-western Europe shows that, in scenarios where a lack of domestic hydrogen supply is forecast, the volume of imports needed from countries such as Scotland ranges from 112–298 TWh in 2030 and 240–1725 TWh in 2050.
Further analysis suggests UK demand of up to 40 TWh[11]. The German government expects to import between 50% and 70% of its 2030 target hydrogen demand of 95-130 TWh, i.e. to import up to 45–90 TWh by 2030[12]. While these targets remain above the range of expected demand put forward by independent analyses, they nevertheless represent a clear policy intent within the developing international hydrogen economy. Countries like Belgium, Italy and the Netherlands have also included imports in their hydrogen strategies[13]. Aligned with this, our export intentions align with an increasing focus within Europe on the role of hydrogen imports via the North Sea and Baltic.[14]
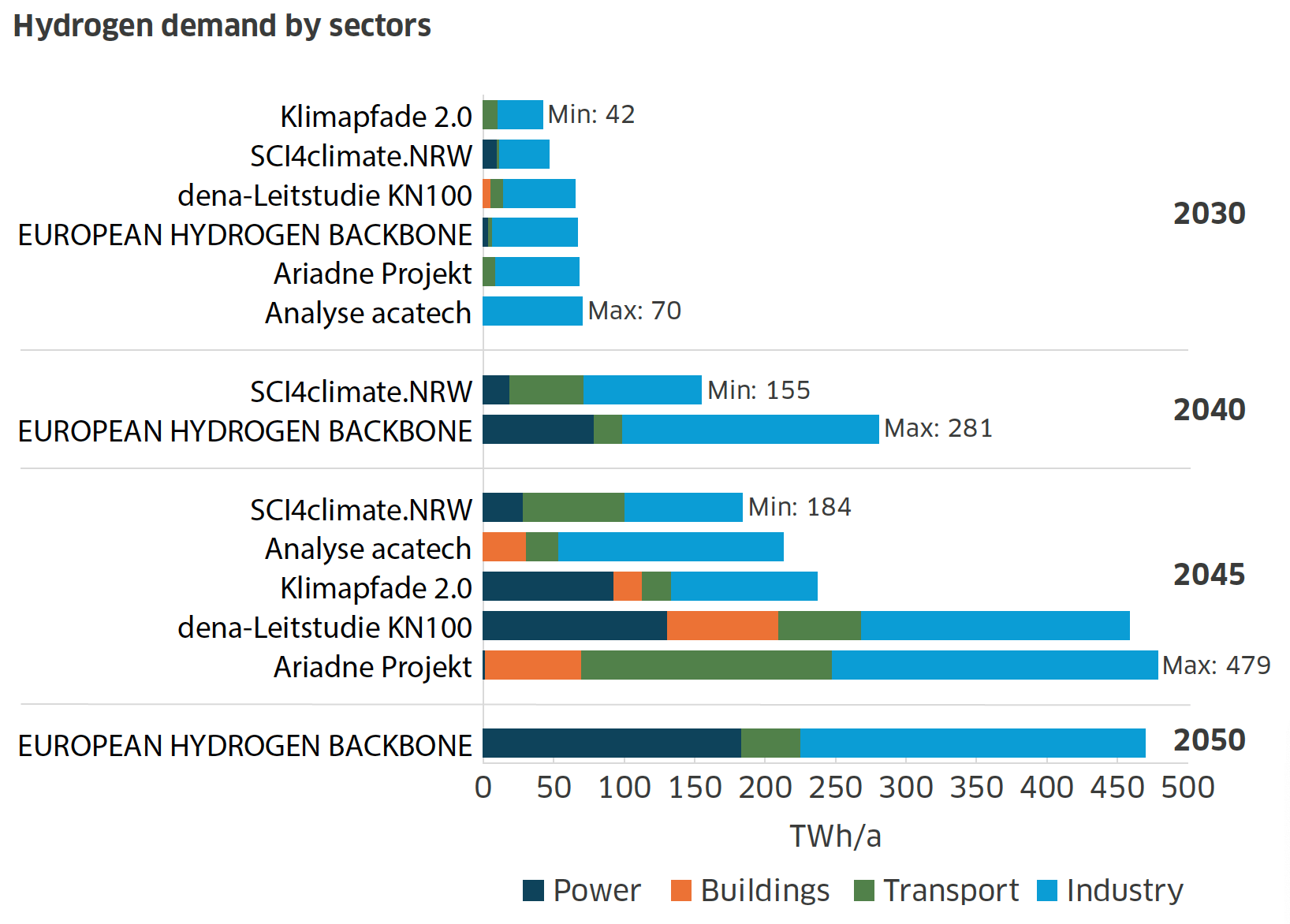
| Power | Buildings | Transport | Industry | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2030 | ||||
| Klimapfade 2.0 | 10 | 32 | ||
| SCI4climate.NRW | 9 | 2 | 36 | |
| dena-Leitstudie KN100 | 5 | 9 | 51 | |
| European Hydrogen Backbone | 3 | 3 | 61 | |
| Ariadne Projekt | 8 | 60 | ||
| Analyse acatech | 70 | |||
| 2040 | ||||
| SCI4climate.NRW | 18 | 53 | 84 | |
| European Hydrogen Backbone | 78 | 20 | 183 | |
| 2045 | ||||
| SCI4climate.NRW | 28 | 72 | 84 | |
| Analyse acatech | 30 | 23 | 160 | |
| Klimapfade 2.0 | 92 | 20 | 21 | 104 |
| dena-Leitstudie KN100 | 130 | 79 | 59 | 191 |
| Ariadne Projekt | 1 | 68 | 178 | 232 |
| 2050 | ||||
| European Hydrogen Backbone | 183 | 42 | 245 | |
Source: Net Zero Technology Centre and Cruh21, May 2024
Contact
Email: William.Gray@gov.scot
There is a problem
Thanks for your feedback