User Guide to Recorded Crime Statistics in Scotland
Provides detailed information on the Recorded Crime in Scotland statistical bulletin series. It is designed to be a useful reference guide with explanatory notes regarding issues and classifications which are crucial to the production and presentation of crime statistics in Scotland.
16. Classification of crimes and offences
Charge codes are issued by the Crown Office and Procurator Fiscal Service (COPFS). They are used to classify crimes and offences based on the relevant section of legislation that they fall under. The detailed list of charge codes as approved by the COPFS is maintained and updated on a monthly basis by the Scottish Government. The process for the creation and maintenance of the charge code list is detailed in Figure 16.1 below.
Charge codes are mapped to crime codes. The crime code list is split into nine crime and offence groups. The first six are referred to as crimes and the remaining three as offences. The nine crime and offence groups are split into 50 crime and offence categories, referred to as the ‘top 50’ categories, that are used in the presentation of recorded crime data. These ‘top 50’ categories along with the main types of crimes and offences included in each of the ‘top 50’ categories, are detailed in section 16.3 below.
A full list of all the crime codes, around 500, used by the Scottish Government to classify crimes and offences can be accessed in Excel format in the Supporting Documents.
As highlighted in 14.3.1, the overall long term comparability of offence crime codes have been affected when Police Scotland was created. The crime codes affected are highlighted in the Excel file.
16.1 Maintenance of the charge code list
Figure 16.1 details the process for the creation and maintenance of the charge code list, with further detail included in Table 16.1.
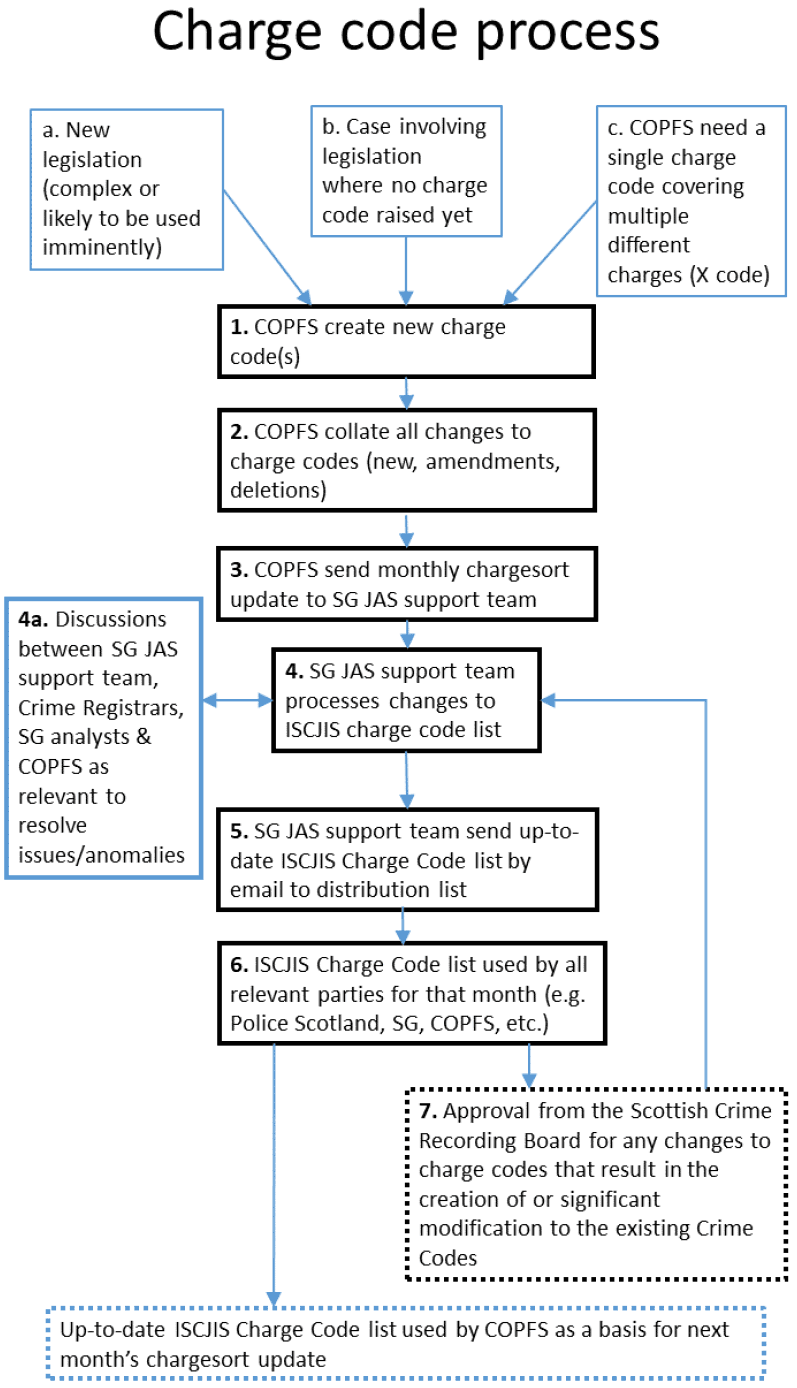
Process for the creation and maintenance of the charge code list
1. Introduction of new charge codes - COPFS generate the 16 digit charge (JD) codes. This can be as a result of:
a. New legislation - Pro-actively generate new charge codes in advance (either when legislation is particularly complex, or when cases are likely to arise quite promptly).
b. New legislation - When a case has arisen which requires a part of legislation that a charge code has not previously been generated for (i.e. await a case to come through the system as there may not be any such case for quite some time).
Note: generally COPFS make the decision whether to pro-actively generate new charge codes in advance or to wait, but ad hoc discussion can be prompted by Scottish Government analysts, Police Scotland and/or Crime Registrars for the pro-active creation of charge codes as and when felt necessary.
c.
- When COPFS require a single charge code to encapsulate a combination of charges. These are referred to as “X codes”, e.g. NONC000000000002 - Abduction, Assault to Severe Injury, Permanent Disfigurement, Permanent Impairment & to Danger of Life.
- X codes are used by COPFS, and are then shared electronically with, and used by, all Criminal Justice partners dealing with the case thereafter (e.g. the Scottish Courts and Tribunals Service and the Criminal History System).
- The need for X codes is legal in nature, although the reasons will differ in each case. One consequence is that a jury is required to return only one verdict covering all the circumstances of the case, rather than separate verdicts. It is also possible that the choice of charge may allow certain evidence to be led in relation to the joint charge that might not be admissible in respect of the individual charges.
- X codes are re-used when available, and so only new combinations of charges result in the creation of a new X code. In general, X codes are only used for the most serious cases, and so the overall number of X codes are not likely to grow dramatically.
- As X codes are ISCJIS charge codes, they are rightly included in the monthly charge code update.
- In circumstances where COPFS issue a new "X" code, it is likely that the Police Scotland case was reported to the PF using the separate ISCJIS codes.
- Police Scotland do not use X codes for recording purposes on those legacy crime systems which record crime using ISCJIS codes. X codes may be available for reporting cases to the PF in areas which have stand-alone case systems, but this does not affect recorded crime. X codes cannot be incorporated into Recorded Crime statistics as they incorporate multiple crimes & can cross categories/groups.
- However, as the ISCJIS-SJGD mappings are issued monthly and invariably X codes are issued incrementally as Fastpaths outwith the main monthly charge code update, an X code could be used by an officer to record a crime in the time between issue and the main monthly charge code update (up to four weeks) when it is known that a specific charge code will be "X" mapped. Such an error can easily be corrected if discovered at the time but, on the rare occasion when it is not noticed, an unrecorded statistic can slip through the net. This is only applicable in three Police Scotland Divisions (North East, Forth Valley and Fife, i.e. those that use CrimeFile as their crime recording system and therefore record crimes using ISCJIS charge codes). Crime Registrars North and East have put checks in place to ensure that this does not happen.
- For Court Proceedings statistical recording purposes, the Scottish Government Support team decide which is the most serious of the multiple charges in an X code and allocate the appropriate crime code accordingly, i.e. the main charge which will receive the most serious sentence if convicted (if the multiple charge contains an ‘attempted’ crime and a ‘successful’ less serious crime, then the crime code for the ‘successful’ crime is usually allocated). e.g. (with main crime underlined) 0HAM0ABD0ROBAMUR - Hamesucken, Abduction, Robbery, Attempted Murder.
2. Collate changes to charge codes
COPFS collate on their system a list of all changes to charge codes required for that month, including any new codes, amendments and deletions (i.e. obsolete codes).
3. Send changes to the Scottish Government JAS support team
COPFS send a monthly update to the Scottish Government Justice Analytical Services support team.
- Amendments could be the result of decisions made/agreed by COPFS, Crime Registrars and/or the Scottish Crime Recording Board.
4. Processing changes
The JAS support team processes all changes on the main ISCJIS Charge Code list.
- Each charge code is mapped to a specific crime code (JD code) as per the crime/offence classifications used by the National Statistics.
- As previously confirmed, X codes cannot be mapped to a specific crime code.
- “M codes” are a further type of charge code which include a modifier. Normally , a single charge code can only map to one, and only one, crime code, but a modifier allows a single charge code to differentiate between multiple options, e.g. many SOSA crimes are split by male/female and so have 2 crime codes [1 male, 1 female], but only one charge code exists that covers both.
- M codes are essentially used to split ISCJIS charge codes into specific crime categories where a single charge would suffice for reporting a case to COPFS. E.g. when the SOSA 2009 legislation was passed, the Scottish Government gave a commitment that statistics would be provided on the gender and age of victims, resulting in M codes being created for several SOSA crimes. Another example is the Theft by Housebreaking charge code, which uses three modifiers of Domestic Dwelling, Domestic Non-Dwelling and Other. The SOSA M codes are supplied by the Police to the COPFS and are the only modifiers on the COPFS database specifically required for statistical, rather than legal, purposes.
- Note: both the police and COPFS use the term Modifier relating to charge codes in different ways. Charge codes used by COPFS can include different modifiers for legal purposes, but these are not the same as the M codes used in Recorded Crime, e.g. where a knife is present but there is no evidence of this being used.
- The Scottish Government Support team are able to allocate a specific crime code against M codes for Criminal Proceedings statistical recording purposes, as COPFS and the courts only need the main charge details, and do not need the modifier information. The gender of the victim is not required for Criminal Proceedings statistics, only the gender of the perpetrator.
a. Any issues/anomalies are queried and resolved through discussion with COPFS, Crime Registrars & Scottish Government analysts.
5. Distribution of updated charge codes
The Scottish Government JAS support team distributes the up-to-date ISCJIS Charge Code list by email to the agreed list which includes COPFS, Police Scotland Crime Registrars, individuals within Police Scotland, the Scottish Police Authority and relevant individuals within partner justice organisations.
6. Usage of charge codes
Crime Recording - Police record crimes against each individual charge code where the system permits, and on the remainder of systems it is recorded against the relevant section of legislation, for it to be subsequently mapped to the relevant crime code.
7. Notification of new or modified crime codes to users
Any changes to charge codes that result in the creation of new, or significant modification to existing, crime codes require approval from the Scottish Crime Recording Board. The Board take a particular interest in any impact of proposed changes to statistical continuity (in particular between the different groups used to classify crimes and offences). Once agreed, JAS statisticians will notify statistical users.
16.2 Structure of crime and offence classifications
After extensive consultation with stakeholders and users (for more detail see consultation chapter), the Scottish Crime Recording Board approved an update to the structure of crime and offence classifications in 2022. The June 2022 publication of the National Statistics annual bulletin Recorded Crime in Scotland, 2021-2022 was the first time the new grouping structure was used to present the statistics.
These changes are outlined in section 16.2.19, with the new structure detailed in section 16.3.
Changes to both the magnitude of groups and the trend over time were analysed and are provided in the Technical Report on the statistical impact of changing to the new groups section of the Summary of responses report.
There was no change to the coverage of crimes and offences in the Recorded Crime in Scotland bulletin series, all changes are purely presentational and have no impact on how a case is investigated or prosecuted. All changes were backdated within the statistics so that there is no discontinuity to the time series, and for the year of 2021/22 only, we published tables using the old groups within the bulletin.
If any crime codes are merged, all crimes and offences that would have previously been recorded under the individual crime codes will still be recorded under the new combined crime code.
16.2.1 Changes to crime and offence classifications
Details of changes within the crime and offence classifications from 2004-05 onwards are shown below; this includes any known future changes. The Scottish Crime Recording Board makes any decisions about the addition or removal of any crime codes. The changes are shown in the years in which they were implemented.
16.2.2 2004-05
The introduction of the Scottish Crime Recording Standard (SCRS) in 2004-05 has helped maintain a consistent approach to recording crime. For further information on the SCRS, please see the Scottish Crime Recording Standard chapter. As anticipated this increased the numbers of minor crimes recorded by the police, such as minor crimes of vandalism and minor thefts. However, it was not anticipated that the SCRS would have a notable impact on the figures for more serious crimes such as Serious assault, Sexual assault, Robbery or Housebreaking.
Unfortunately it was not possible to estimate the exact impact of the new recording standard on the recorded crime figures because around the time that the new standard was implemented, police also introduced centralised call centres which encouraged the reporting of incidents to the police.
16.2.3 2005-06
The top 35 category Petty assault was renamed Minor assault.
The following new crime codes were introduced as a result of new legislation and there was a requirement to identify these crimes and offences separately:
Group 1 – Non-sexual crimes of violence:
- 11007: Female genital mutilation – Prohibition of Female Genital Mutilation (Scotland) Act 2005
Group 2 – Sexual crimes:
- 18014: Grooming of children for purposes of sexual crimes – Protection of Children and Prevention of Sexual Offences (Scotland) Act 2005
Group 5 – Other crimes:
- 35005: Obstruct or hinder other emergency worker in pursuance of duty – Emergency Workers (Scotland) Act 2005
- 39016: Breach of parenting order – Antisocial Behaviour etc. (Scotland) Act 2004
Group 6 – Miscellaneous offences:
- 47006: Minor assault of an emergency worker – Emergency Workers (Scotland) Act 2005
- 47007: Antisocial behaviour offences – Antisocial Behaviour etc. (Scotland) Act 2004
- 50011: Offences relating to persons disqualified from working with children – Protection of Children (Scotland) Act 2003
- 50012: Prevent a person feeding a baby milk in a public place – The Breastfeeding etc. (Scotland) Act 2005
- 50013: Offences against selling spray paint to children – Antisocial Behaviour etc. (Scotland) Act 2004
- 85034: Antisocial behaviour, landlord offences – Antisocial Behaviour etc. (Scotland) Act 2004
16.2.4 2006-07
The following new crime codes were introduced as a result of new legislation and there was a requirement to identify these crimes separately:
Group 2 – Sexual crimes:
- 18015: Procuration of sexual services from child under 18 – Protection of Children and Prevention of Sexual Offences (Scotland) Act 2005
- 18016 :Procuration of child under 18 for pornography – Protection of Children and Prevention of Sexual Offences (Scotland) Act 2005
Group 5 – Other crimes:
- 39017: Breach of risk of sexual harm order (SHO) or interim risk of SHO – Protection of Children and Prevention of Sexual Offences (Scotland) Act 2005
- 39018: Breach of football banning order – Police Public Order and Criminal Justice (Scotland) Act 2006
16.2.5 2007-08
Within the Other miscellaneous offences category in Group 6 – Miscellaneous offences the crime code 48000: False calls to emergency services and bomb hoax was removed and replaced with two separate crime codes: 48001: False or hoax calls to emergency services and 48002: Bomb hoaxes. This change will not affect comparability over time.
The following new crime codes were introduced as a result of new legislation and there was a requirement to identify these crimes and offences separately:
Group 2 – Sexual crimes:
- 18017 Soliciting services of person engaged in prostitution – Prostitution (Public Places) (Scotland) Act 2007
Group 6 – Miscellaneous offences:
- 85035: Offences relating to working with vulnerable adults – Adult Support and Protection (Scotland) Act 2007
16.2.6 2008-09
The following new crime codes were introduced as a result of new legislation and there was a requirement to identify these crimes separately:
Group 1 – Non-sexual crimes of violence:
- 3004: Causing death by careless driving – Road Safety Act 2006
- 3005: Illegal driver involved in fatal accident – Road Safety Act 2006
- 3006: Corporate homicide – Corporate Manslaughter and Corporate Homicide Act 2007
16.2.7 2009-10
Within the Vandalism etc. category in Group 4 – Fire-raising, vandalism etc. the crime code 33001: Vandalism, reckless damage and malicious mischief was removed and replaced with three separate crime codes: 33012: Vandalism, 33013: Reckless damage and 33014: Malicious mischief. This change will not affect comparability over time.
The crime code 59003: Taking, distribution etc. indecent photos of children was introduced and included in Group 6 – Miscellaneous offences, within the Other miscellaneous offences category. This was done so that such offences could be separately identified. Previously such offences would have been included within the same top 35 category, under the crime code 59001: Handling obscene material. It was not possible to disaggregate any crimes that would have been recorded as 59003: Taking, distribution etc. indecent photos of children prior to 2009-10. As some offences, that would have previously been classified as 59001: Handling obscene material, will no longer be classified as such, caution should therefore be taken when comparing this crime code with previous years.
The following new crime codes were introduced as a result of new legislation and there was a requirement to identify these crimes and offences separately:
Group 5 – Other crimes:
- 39019: Breach of adult at risk banning order – Adult Support and Protection (Scotland) Act 2007
- 39020: Breach of violent offender order – Criminal Justice and Immigration Act 2008
Group 6 – Miscellaneous offences:
- 60008: Refusing to quit licensed premises – Licensing (Scotland) Act 2005
- 85036: Offences under the Charities and Trustees Investment (Scotland) Act 2005 – Charities and Trustees Investment (Scotland) Act 2005
Following the introduction of the crime code 60008: Refusing to quit licensed premises there was a decrease in the number of offences recorded under the crime code 60006: Disorderly on licensed premises in 2009-10. Some offences that would have previously been recorded as 60006: Disorderly on licensed premises were now recorded as 60008: Refusing to quit licensed premises. It is not possible to quantify the number of offences that were recorded differently following the introduction of the crime code 60008: Refusing to quit licensed premises. As a result, caution should therefore be taken when comparing the crime code 60006: Disorderly on licensed premises with previous years.
16.2.8 2010-11
The Sexual Offences (Scotland) Act 2009 came into force on 1 December 2010. The Act replaces a number of common law crimes including Rape, Clandestine injury to women and Sodomy with new statutory sexual crimes. The Act provides a statutory description of consent, which is defined as free agreement and provides a non-exhaustive list of factual circumstances during which consent will be deemed to be absent.
The Act created a number of new ‘protective’ offences, which criminalise sexual activity with children and mentally disordered persons. There are separate offences concerning young children (under 13 years) and older children (13-15 years).
The new legislation only applies to offences committed from 1 December 2010. Any offences committed prior to this date will be recorded using previous legislation.
The new legislation resulted in some increases in Sexual crimes. However, it is likely that the effect has been to change the distribution of these crimes among the subcategories. For example, some crimes previously categorised as Lewd and libidinous practices will now be classified as Sexual assault.
The introduction of the new legislation resulted in some crimes that would previously have been classified in either the Breach of the peace or Other miscellaneous offences top 35 categories being classified as Sexual crimes. Most of these are now classed in the top 35 category Other sexual crimes. However, it is not possible to quantify the number of crimes that this change affects.
Any sexual crime which occurred prior to 1 December 2010 will be recorded in line with the appropriate legislation in place at that time. If the conduct occurred both prior to and after 1 December 2010 the appropriate offences under the old and new legislation are recorded. Caution should therefore be taken when comparing Sexual crimes with previous years.
Within Group 2 – Sexual crimes the top 35 categories Indecent assault and Lewd and indecent behaviour were combined and renamed Sexual assault. In addition a new top 35 category, Prostitution, was added to Group 2 – Sexual crimes. The Prostitution category only contained one crime code when it was introduced, 18010: Offences related to prostitution. Further information on the changes in the top 35 categories within Group 2 – Sexual crimes can be accessed.
The crime code 18011: Clandestine injury was removed due to the introduction of new crime codes, as a result of the implementation of the Sexual Offences (Scotland) Act 2009, where crimes previously classified as this crime could now be classified elsewhere.
The following new crime codes were introduced within Group 2 – Sexual crimes as a result of implementation of the Sexual Offences (Scotland) Act 2009:
- 14001: Rape of male (16+)
- 14002: Rape of female (16+)
- 14003: Rape of older male child (13-15 years)
- 14004: Rape of older female child (13-15 years)
- 14005: Rape of young male child (Under 13)
- 14006: Rape of young female child (Under 13)
- 15001: Assault with intent to rape male (16+)
- 15002: Assault with intent to rape female (16+)
- 15003: Assault with intent to rape older male child (13-15)
- 15004: Assault with intent to rape older female child (13-15)
- 15005: Assault with intent to rape young male child (under 13)
- 15006: Assault with intent to rape young female child (under 13)
- 16001: Sexual assault by penetration of male (16+)
- 16002: Sexual assault by penetration of female (16+)
- 16003: Sexual assault by penetration of male (13-15 years)
- 16004: Sexual assault by penetration of female (13-15 years)
- 16005: Sexual assault of male (16+)
- 16006: Sexual assault of female (16+)
- 16007: Sexual assault of older male child (13-15 years)
- 16008: Sexual assault of older female child (13-15 years)
- 16009: Sexual coercion of male (16+)
- 16010: Sexual coercion of female (16+)
- 16011: Sexual coercion of older male child (13-15 years)
- 16012: Sexual coercion of older female child (13-15 years)
- 16013: Coercing a person into being present/ looking at sexual activity
- 16014: Communicating indecently
- 16015: Assault by penetration of young male child (under 13)
- 16016: Assault by penetration of young female child (under 13)
- 16017: Sexual assault of young male child (under 13)
- 16018: Sexual assault of young female child (under 13)
- 16019: Cause young male child (under 13) to participate in sexual activity
- 16020: Cause young female child (under 13) to participate in sexual activity
- 16021: Cause young child to be present/ look at sexual activity (under 13)
- 16022: Communicating indecently with young child (under 13)
- 16023: Sexual exposure to a young child (under 13)
- 16024: Voyeurism young child (under 13)
- 16025: Intercourse with older male child (13-15)
- 16026: Intercourse with older female child (13-15)
- 16027: Penetrative sexual activity with older male child (13-15)
- 16028: Penetrative sexual activity with older female child (13-15)
- 16029: Sexual activity with older male child (13-15)
- 16030: Sexual activity with older female child (13-15)
- 16031: Cause older male child (13-15) to participate in sexual activity
- 16032: Cause older female child (13-15) to participate in sexual activity
- 16033: Older male child (13-15) engaging in sexual conduct with another older child
- 16034: Older female child (13-15) engaging in sexual conduct with another older child
- 16035: Causing an older child (13-15) to be present/ look at sexual activity
- 16036: Communicate indecently older child (13-15)
- 16037: Sexual exposure older child (13-15)
- 16038: Voyeurism older child (13-15)
- 17003: Sexual exposure
- 17004: Voyeurism
- 18018: Taking, distribution, possession etc. of indecent photos of children
- 18019: Sexual abuse of trust of person under 18
- 18020: Sexual abuse of trust of person of mentally disordered person
- 18023: Administering a substance for sexual purposes
On 6 October 2010, the Criminal Justice and Licensing (Scotland) Act 2010 was implemented. This introduced a statutory provision to combat Threatening or abusive behaviour (section 38). Unlike the common law offence of Breach of the peace, where it is necessary to show a ‘public element’ to the conduct, there is no requirement in this legislation to demonstrate the offending behaviour was in a public place. Section 39 of this Act introduced the specific offence of "stalking". Formerly this offence would have been recorded under the common law offence of Breach of the peace.
Crimes of Stalking and of Threatening and abusive behaviour were included in the Other miscellaneous offences category in Group 6 – Miscellaneous offences, whereas, they would have previously have been included in the Breach of the peace category in Group 6 – Miscellaneous offences.
The following new crime codes were introduced in Group 6 – Miscellaneous offences as a result of implementation of the Criminal Justice and Licensing (Scotland) Act 2010:
- 47008: Threatening or abusive behaviour
- 47009: Offence of stalking
As these two offences would have previously been classified as the crime code 47002: Breach of the peace, caution should therefore be taken when comparing this crime code with previous years.
Within the Vandalism etc. category in Group 4 – Fire-raising, vandalism etc. the crime code 33013: Reckless damage was removed as crimes classified under it should be classified under two other existing crime codes: 33011: Culpable and reckless conduct (not with firearms) or 33012: Vandalism. Caution should therefore be taken when comparing these two crime codes with previous years.
Within Group 3 – Crimes of dishonesty, there was a reclassification of thefts from ATMs and fuel pumps, which took effect from 1 April 2010. Prior to this such crimes would have been recorded within the Theft by opening lockfast places (OLP) category under the crime code 20001: Theft by opening lockfast places (excluding motor vehicle). Such crimes will now be classified under the crime code 25000: Fraud, within the Fraud category. Caution should therefore be taken when comparing these two crime codes and top 35 categories with previous years.
In addition within Group 3 – Crimes of dishonesty, there was also a reclassification of crimes of forgery and uttering, which also took effect from 1 April 2010. Prior to this such crimes would have been recorded within the Other dishonesty category under the crime code 26000: Forgery (other). Such crimes will now be classified under the crime code 25000: Fraud, within the Fraud category. Caution should therefore be taken when comparing these two crime codes and top 35 categories with previous years.
The following new crime codes were introduced as a result of new legislation and there was a requirement to identify these crimes separately:
Group 1 – Non-sexual crimes of violence:
- 11008: Offences relating to Serious Organised Crime – Criminal Justice and Licensing (Scotland) Act 2010
Group 5 – Other crimes:
- 38019: Protection of vulnerable groups – The Protection of Vulnerable Groups Act 2007
The following new crime code was introduced as this was the first year a crime was recorded under the relevant legislation:
Group 5 – Other crimes:
- 34004: United Nations Sanctions Offences – Iraq (United Nations Sanctions) Order 2000
16.2.9 2011-12
On 1 March 2012, the Offensive Behaviour at Football and Threatening Communications Act 2012 was implemented. The Act introduced two new offences, Offensive behaviour at football and Threatening communications. The following new crime codes were introduced in Group 6 – Miscellaneous offences as a result of implementation of the Offensive Behaviour at Football and Threatening Communications Act 2012:
- 47010: Offensive behaviour at football (under the Offensive Behaviour at Football and Threatening Communications Scotland Act 2012)
- 47011: Threatening communications (under the Offensive Behaviour at Football and Threatening Communications Scotland Act 2012)
The crime code 59003: Taking, distribution etc. indecent photos of children was moved from the Other miscellaneous offences category in Group 6 – Miscellaneous offences to the Other sexual crimes category in Group 2 – Sexual crimes, following the introduction of the similar crime code 18018: Taking, distribution, possession etc. of indecent photos of children, in 2010-11. This change was back revised to when the crime code 59003: Taking, distribution etc. indecent photos of children was introduced in 2009-10. This means that since 2009-10 all such crimes are now classified as crimes and not offences.
In April 2011, crimes of Handling an offensive weapon and Drug crimes in prisons were reclassified from the Other miscellaneous offences category in Group 6 – Miscellaneous offences to the categories of Handling offensive weapons and Drugs in Group 5 – Other crimes respectively. This means that prior to 2011-12 these prison related crimes would have been classified as offences. Therefore caution should be used when making any comparison over time for the crime code 85001: Prisons (Scotland) Act 1989 (not elsewhere classified), where the crimes of Handling an offensive weapon and Drug crimes in prisons would have previously been classified. For 2011-12, it was not possible to disaggregate either the crimes of Handling an offensive weapon or Drug crimes that took place in prison from the crimes that did not take place in prisons.
There were a number of changes to the crime groups and top 36 categories:
- Group 2 was renamed Sexual offences, in line with the naming convention of the Sexual Offences (Scotland) Act 2009, from Crimes of indecency.
- The top 35 category Serious assault etc. was split into two new categories: Homicide and Attempted murder and serious assault.
- The top 35 category Prostitution was replaced by a new category called Offences associated with prostitution. This includes the crimes in the old Prostitution category as well as the following crimes that were previously included in the Other sexual crimes category: Soliciting services of person engaged in prostitution, Brothel keeping, Immoral traffic and Procuration.
- The top 35 category Other sexual crimes includes: Other sexually coercive conduct, Other sexual crimes involving 13-15 year old children, Taking, distribution, possession etc. of indecent photos of children, Incest, Unnatural crimes, Public indecency and Sexual exposure.
- The top 35 category Minor assault was renamed Common assault. In turn crime codes 47001: Minor assault and 47006: Minor assault of an emergency worker were similarly renamed 47001: Common assault and 47006: Common assault of an emergency worker respectively.
- The top 35 category Breach of the peace was changed to Breach of the peace etc. The category has been renamed as it now includes the following offences in addition to Breach of the peace: Threatening or abusive behaviour, Offence of stalking, Offensive behaviour at football (under the Offensive Behaviour at Football and Threatening Communications Scotland Act 2012) and Threatening communications (Offensive Behaviour at Football and Threatening Communications Act 2012). Threatening or abusive behaviour and the Offence of stalking were included in the Other miscellaneous offences category in 2010-11. As these offences would have previously been classified as crime code 47002: Breach of the peace, any comparisons over time for the offence of Breach of the peace should be made using the top 35 category Breach of the peace etc.
- The top 35 category Drunk driving was renamed Driving under the influence, to reflect the fact that this category includes offences relating to driving while under the influence of drugs as well as offences relating to drink driving.
The crime code 4001: Causing injury etc. by culpable and reckless conduct was introduced and included in Group 1 – Non-sexual crimes of violence, within the Attempted murder and serious assault category. This was done so that such crimes could be separately identified. Previously such crimes would have been included within the same top 35 category, under the crime code 4000: Serious assault. This change will not affect comparability over time.
The following new crime codes were introduced as a result of new legislation and there was a requirement to identify these crimes separately:
Group 5 – Other crimes:
- 39021: Breach of domestic abuse interdict – Domestic Abuse (Scotland) Act 2011
- 39022: Breach of forced marriage protection order – Forced Marriage etc. (Protection and Jurisdiction) (Scotland) Act 2011
16.2.10 2012-13
From April 2012, it was possible to disaggregate crimes of Handling an offensive weapon and Drug crimes in prisons. This resulted in the introduction of four new crime codes in Group 5 – Other crimes:
43004: Having in a prison an article with a blade or point
43005: Possession of a firearm in a prison
43006: Possession of an offensive weapon (not elsewhere specified) in a prison
44006: Bringing drugs into prison
Within the Other sexual crimes category in Group 2 – Sexual crimes, the crime code 59003: Taking, distribution etc. indecent photos of children was combined with 18018: Taking, distribution, possession etc. of indecent photos of children and then removed. This change will not affect comparability over time.
16.2.11 2013-14
Prior to 2013-14, Group 2 was called Sexual offences, as this corresponds to the name of the legislation, Sexual Offences (Scotland) Act 2009, covering these crimes. This led to some confusion as to whether this group was being included in crimes or offences. To emphasise that these are crimes, as they always have been, Group 2 was renamed Sexual crimes. The corresponding name changes were made to the other top 35 categories and individual crime codes in Group 2.
The top 35 category Homicide was renamed Homicide etc. to reflect that this category contains the crimes of Murder and Culpable homicide (common law), as well as the crimes of Causing death by dangerous driving, Death by careless driving when under influence of drink or drugs, Causing death by careless driving, Illegal driver involved in fatal accident and Corporate homicide. The change in the category name was to avoid confusion with the Homicide in Scotland bulletin. In the Homicide in Scotland bulletin, the crimes of Murder and Culpable homicide (common law) are collectively referred to as Homicide.
The top 35 category Drunkenness was renamed Drunkenness and other disorderly conduct. The name change was to reflect better the type of offences that are included in this category. In addition, the crime code 72008: Consumption of alcohol in designated places, byelaws prohibited was moved to this top 35 category from the Other miscellaneous offences category. This was done as the Drunkenness and other disorderly conduct category more accurately reflects the nature of the offences recorded under the crime code 72008: Consumption of alcohol in designated places, byelaws prohibited. This change was backdated so that all offences recorded as crime code 72008: Consumption of alcohol in designated places, byelaws prohibited are now included in the Drunkenness and other disorderly conduct category. Therefore, comparisons over time for these two top 35 categories have not been affected.
Three new categories were added to the then top 32 categories, making it the top 35 categories. The three new categories, and the rationale behind their inclusion are:
- The category Urinating etc. was added. This category contains one crime code, 47003: Urinating etc. Previously this crime code would have been included in the Other miscellaneous offences category. This was done so that the large number of offences of Urinating etc. could be separately identified and not just classified in the Other miscellaneous offences category. Other categories like the Other miscellaneous offences category are intended for grouping together crimes and offences that are not recorded in large numbers. This change has been backdated so that all offences recorded as crime code 47003: Urinating etc. are now classified in the Urinating etc. category. Therefore, comparisons over time for these two top 35 categories have not been affected.
- The category Seat belt offences was added. This category contains one crime code, 323000: Seat belt offences. Previously this crime code would have been included in the Other motor vehicle offences category. This was done so that the large number of seat belt related offences could be separately identified and not just classified in the Other motor vehicle offences category. Other categories like the Other motor vehicle offences category are intended for grouping together crimes and offences that are not recorded in large numbers. This change has been backdated so that all offences recorded as crime code 323000: Seat belt offences are now classified in the Seat belt offences category. Therefore, comparisons over time for these two top 35 categories have not been affected.
- The category Mobile phone offences was added. This category contains one crime code, 324000: Mobile phone offences. Previously this crime code would have been included in the Other motor vehicle offences category. This was done so that the large number of driving related mobile phone offences could be separately identified and not just classified in the Other motor vehicle offences category. Other categories like the Other motor vehicle offences category are intended for grouping together crimes and offences that are not recorded in large numbers. This change has been backdated so that all offences recorded as crime code 324000: Mobile phone offences are now classified in the Mobile phone offences category. Therefore, comparisons over time for these two top 35 categories have not been affected.
Within the Other miscellaneous offences category in Group 6 – Miscellaneous offences, the crime code 51010: Dangerous Dogs, failure to control, supervise, destroy was combined with the crime code 51012: Offences involving dangerous dogs and then removed. This change will not affect comparability over time.
16.2.12 2014-15
The crime code 18024: Possession of extreme pornography was introduced and included in Group 2 – Sexual crimes, within the Other sexual crimes category. This was done so that such crimes could be separately identified. Previously such crimes would have been classified as offences in the Group 6 – Miscellaneous offences category Other miscellaneous offences, under the crime code 59001: Handling obscene material. It was not possible to disaggregate any crimes that would have been recorded as 18024: Possession of extreme pornography prior to 2014-15. As some offences that would have previously been classified as 59001: Handling obscene material will no longer be classified in this way, caution should therefore be taken when comparing this crime code with previous years.
The following new crime code was introduced as a result of new legislation and there was a requirement to identify this offence separately:
Group 6 – Miscellaneous offences:
- 85037: Failure to comply with a Property Factor Enforcement Order (PFEO) – Property Factors (Scotland) Act 2011
16.2.13 2015-16
The following new crime codes were introduced in the Other violence category of Group 1 – Non-sexual crimes of violence as a result of new legislation, and there was a requirement to identify these crimes separately:
- 4002: Illegal driver, disqualified/unlicensed etc. causing serious injury
- 11009: Forced Marriage
16.2.14 2016-17
The following new crime codes were introduced as a result of new legislation, the Human Trafficking and Exploitation (Scotland) Act 2015, which came into force on 31 May 2016:
Group 1 – Non-sexual crimes of violence:
- 11010: Slavery or forced labour
- 11011: Human organ offences
Group 5 – Other crimes:
- 39023: Breach of a trafficking & exploitation order
The existing crime code 18009 – Immoral traffic (Group 2 – Sexual Crimes) will also be used to record some of the charges resulting from the new Act. No significant impact is envisaged for Group 2 as the new offences from the Act replace existing offences included within this group.
The following new codes were introduced as a result of new legislation, the Psychoactive Substances Act 2016:
Group 5 – Other crimes:
- 44007: Psychoactive substance: production, import/export, supply or possession in custody
- 44008: Psychoactive substance: other offences
The following new crime code was introduced following the decision that 11008: Offences relating to serious organised crime, which previously sat within Group 1 – Non-sexual crimes of violence, should be transferred to the Other crimes category within Group 5 – Other crimes. The decision was based on the fact that these are not technically violent crimes, and any associated violent crime related to an incident of serious organised crime would already be counted within Group 1:
Group 5 – Other crimes:
- 40001: Offences relating to serious organised crime
As a result, the following crime code has been removed:
Group 1 – Non-sexual crimes of violence:
- 11008: Offences relating to serious organised crime
The following new crime code was introduced as of January 2017 as a result of new legislation, Smoking Prohibition (Children in Motor Vehicles) (Scotland) Act 2016, which came into force in December 2016. It is anticipated that this legislation will, for the most part, be enforced by local authorities, and so do not expect many of these offences to be recorded by Police Scotland.
Group 6 – Miscellaneous offences:
- 50014 – Smoking in car with child
The following new crime code was introduced as of December 2016 as a result of new legislation, Air Weapons and Licensing (Scotland) Act 2015, which came into force in December 2016.
Group 6 – Miscellaneous offences:
- 55001 – Air weapons licensing offences
The following new offence code was introduced following the decision that 59001: Handling obscene material, which previously sat within Group 6 – Miscellaneous Offences, should be split into 2 separate offence codes. One new offence code (59004: Communications Act 2003 (sexual)) to cover sexual communication offences (i.e. the sending of sexual/offensive/obscene/ menacing messages by means of public electronic communications) and the original offence code (59001: Handling obscene material) to cover the displaying or distribution of obscene material, the import of prohibited goods to the UK or the sending of obscene or indecent articles through the post. This decision was based on a desire to identify what proportion of Handling Obscene Material offences were based on sexual communication offences, to support future consideration of the statistical classification of this offence. This change will have no impact on the overall figures for Group 6 – Miscellaneous Offences.
Group 6 – Miscellaneous offences:
- 59004: Communications Act 2003 (sexual)
16.2.15 2017-18
The crime code 11003: Ill treatment of mental patients, within Group 1 – Non-sexual crimes of violence, was renamed to become 11003: Ill treatment and neglect of mental patients and vulnerable adults, following the decision to move offences recorded under 85035: Offences relating to working with vulnerable adults, within Group 6 – Miscellaneous Offences, into Group 1 crimes instead. This had a negligible impact on the overall figures for Group 1 – Non-sexual crimes of violence.
As a result, the following crime code was removed:
Group 6 – Miscellaneous offences:
- 85035: Offences relating to working with vulnerable adults
The following new crime codes will be introduced as a result of new legislation, the Abusive Behaviour and Sexual Harm (Scotland) Act 2016, which is scheduled to come into force during 2017-18.
Group 2 – Sexual crimes
- 16039 – Threatening to disclose an intimate image
- 16040 – Disclosure of an intimate image
It is unclear at this time what impact these changes will have on the overall figures for Group 2 – Sexual crimes, although an increase is anticipated. There is likely to be some impact on the volume of Group 1 – Non-sexual crimes of violence, as crimes involving someone threatening to disclose an intimate image for the purpose of obtaining sexual favours, currently recorded as 7000: Threats and extortion, would move to Group 2. Further, the actual disclosure of someone’s intimate image, currently recorded as 59004: Communications Act 2003 (sexual), would move to Group 2. As detailed below, offences recorded as 59004: Communications Act 2003 (sexual) are being transferred to Group 2 crimes anyway.
The following new crime code will be introduced following the decision that 59004: Communications Act 2003 (sexual), which currently sits within Group 6 – Miscellaneous Offences, should be transferred to the Other sexual crimes category within Group 2 – Sexual crimes. The decision was based on the fact that it is more appropriate for these offences to be recorded as sexual crimes. It is anticipated that this will have a small impact on the number of Group 2 crimes, although some of these crimes may be recorded under the new crime codes as detailed above.
Group 2 – Sexual crimes
- 16041 – Communications Act 2003 (sexual)
The following new crime code will be introduced, which will record crimes like shining a laser pen at an aircraft. It is not anticipated that this will have a significant impact on Group 4 crimes.
Group 4 – Fire-raising, vandalism etc.
- 33016 – Culpable and reckless conduct involving aircraft
As a result of this new crime code, and to ensure consistency, the counting rule for 33011: Culpable and reckless conduct has been changed from “One crime for each incident” to “One crime for each incident unless this involves a vehicle or train in which case a crime will be recorded for each vehicle or train”. This may result in a slight increase, as previously any such conduct that involved more than one vehicle/train would have been recorded as one crime.
The following new crime codes were introduced to enable the separate identification of these crimes, as they were previously included as part of 43003: Having in a public place an article with a blade or point. This change will have no impact on the total for the Handling offensive weapons category.
Group 5 – Other crimes
- 43/07 – Possession of an offensive weapon (not elsewhere specified) in a school
- 43/08 – Having in a school an article with a blade or point
The following new crime codes were introduced following the decision that crimes of handling offensive weapons in public settings will no longer be subsumed when used to commit other criminal activity, as the criminal law views the possession of a weapon in a public setting as a separate crime in its own right. Previously, statistics on handling offensive weapons only included crimes where the perpetrator had not committed further crimes with the weapon. If they had, then the weapon possession would be considered an aggravation of the main crime (e.g. serious assault) and would be ‘subsumed’ into the main crime.
Group 5 – Other crimes
- 43009 – Possession of offensive weapon used in other criminal activity
- 43010 – Having in a public place an article with a blade or point used in other criminal activity
- 43011 – Possession of offensive weapon in a prison used in other criminal activity
- 43012 – Having in a prison an article with a blade or point used in other criminal activity
- 43013 – Possession of offensive weapon in a school used in other criminal activity
- 43014 – Having in a school an article with a blade or point used in other criminal activity
Group 5 – Other crimes
- 44001 – Illegal importation of drugs
- 44002 – Production, manufacture or cultivation of drugs
- 44003 – Supply, possession with intent to supply etc. of drugs
- 44004 – Possession of drugs
- 44005 – Drugs, money laundering related offences
- 44006 – Bringing drugs into prison
- 44007 – Psychoactive Substance: Production, supply or possession in custody
- 44008 – Psychoactive Substance: Other Offences
- 44099 – Drugs, other offences
Etizolam has been classified as a Class C drug by the May 2017 amendment to the Misuse of Drugs Act 1971, along with several other designer benzodiazepine drugs.
16.2.16 2018-19
The Offensive Weapons Act received Royal Assent in May 2019. The Act will make it illegal to possess dangerous weapons in private, and will make it a criminal offence to dispatch bladed products sold online without verifying the buyer is over 18. The Act also makes it an offence to possess a corrosive substance in a public place, and has updated the definition of a flick knife to reflect changing weapons design. The Scottish Crime Recording Board will continue to monitor the implementation of this Act and users will be informed of what impact these changes will have on the presentation of the National Statistics.
During the 2018-19 financial year the Board made changes to the coding of crimes and offences as a result of the Domestic Abuse (Scotland) Act 2018.
The Domestic Abuse (Scotland) Act 2018 came into force on 1st April 2019. The Act created a new offence of abusive behaviour as a course of conduct towards a partner or ex-partner. Previously, any criminal act which formed part of a domestic abuse incident (such as a Common assault or Threatening or abusive behaviour) was included within the statistics under the relevant crime or offence. Where there is evidence of a course of conduct, new crime codes of Domestic abuse against a male or female victim have been created. Existing common law and statutory offences will continue to be used where appropriate in addition to the new crimes, with some exceptions (in particular Threatening and abusive behaviour), which will be included within the new crime.
As a result the following new crime codes have been added to the Crime code list:-
Group 1 – Crimes of violence
- 11012 – Domestic Abuse of MALE
- 11013 – Domestic Abuse of FEMALE
16.2.17 2019-20
Coronavirus restrictions crimes
On 23rd March 2020, a nationwide lockdown was imposed due to the COVID-19 pandemic, with guidelines on movements for some days prior to that. This had a significant impact on daily living which also affected the number of crimes and offences recorded, to varying degrees. To inform users about the volume and type of crimes and offences recorded in Scotland during the pandemic, the Scottish Government introduced a new monthly series of Official Statistics from April 2020 onwards. Recorded Crime in Scotland - gov.scot (www.gov.scot)
The Coronavirus Act 2020 and Health Protection (Coronavirus) (Restrictions) (Scotland) Regulations 2020 were implemented on 25th March and 27th March 2020, respectively, and resulted in new crimes being recorded - for example where someone, who had left the place they were living, did not have a reasonable excuse for this when asked by a police officer, and failed to comply with police advice or instruction to return there.
The following are a list of the new coronavirus codes:-
These have been recorded under a new crime group for Coronavirus restrictions
- 33017 - Coronavirus restrictions
- 33018 - Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Fail to provide info (SPR)
- 33019 - Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Fail to provide info (£60)
- 33020 - Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Fail to provide info (£120)
- 33021 - Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Fail to provide info (£240)
- 33022 - Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Fail to provide info (£480)
- 33023 - Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Provide false/misleading info (SPR)
- 33024 - Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Provide false/misleading info (£60)
- 33025 - Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Provide false/misleading info (£120)
- 33026 - Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Provide false/misleading info (£240)
- 33027 - Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Provide false/misleading info (£480)
- 33028 - Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Fail to quarantine (SPR)
- 33029 - Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Fail to quarantine (£480)
- 33030 - Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Contravene a requirement (SPR)
- 33031 - Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Contravene a requirement (£480)
- 33032 - Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Provide false/misleading passenger info (SPR)
- 33033 - Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Provide false/misleading passenger info (£480)
- 33034 - Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Obstruct (passenger info) (SPR)
- 33035 - Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Obstruct (passenger info) (£60)
- 33036 - Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Obstruct (passenger info) (£120)
- 33037 - Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Obstruct (passenger info) (£240)
- 33038 - Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Obstruct (passenger info) (£480)
- 33039 - Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Obstruct (quarantining) (SPR)
- 33040 - Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Obstruct (quarantining) (£480)
- 33041 - Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Operator fail to provide passenger info
- 33042 - Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Testing offences
Driving under the influence
Changes to the Road Traffic Act 1988 which introduced new offences of driving or being in charge of a motor vehicle with concentration of a specified controlled drug above a specified limit came into force on 21st October 2019. While offences of driving or being in charge of a motor vehicle while impaired through alcohol or drugs already existed, evidence of impaired driving is not required for the new offences. This is likely to have resulted in additional offences being recorded in relation to drug driving within the Driving under the influence category (from October 2019).
Group 7: Motor vehicle offences
New crime codes:-
Driving motor vehicle while under influence of controlled drug above prescribed limit – new crime code 301007
In charge of motor vehicle while under influence of controlled drug above prescribed limit – new crime code 301008
16.2.18 2020-21
Cross-border crimes
A procedural change was made in April 2020 to how crimes which could involve a victim and a perpetrator in different physical locations (e.g. cyber-enabled crimes) are recorded. Prior to the 1st April 2020, these statistics excluded any crime with a victim in Scotland and a perpetrator who was confirmed by the police to be outside the United Kingdom when the crime took place. Following a recommendation by Her Majesty’s Chief Inspectorate for Constabulary in Scotland (HMICS) to review recording practice in this area12, the Scottish Crime Recording Board approved a change so that from the 1st April these crimes are now included in the statistics. It should be noted that those cases with only a suspicion or insufficient evidence to confirm that the perpetrator was outside the UK were always included.
This change is likely to lead to the recording of additional crimes for those types of crime which could be committed using digital technologies. In 2020-21, we estimated an additional 1,160 crimes being recorded, which represents less than 1% of all crime recorded in Scotland that year.
16.2.19 2021-22
Following extensive consultation (see Consultation section for more detail) the Scottish Crime Recording Board approved a number of changes to the way recorded crime statistics are classified and presented.
The Scottish Crime Recording Board decided that the previous set of crime and offence groups would be replaced. The new grouping structure retains a similar number of groups to the previous structure (9 vs 8), but provides more detail at the second level of disaggregation, with a 'top-50' category structure, compared to the previous ‘top-38’. The new grouping structure is presentented in section 16.3 Current Crime Code Classification.
The changes which have been made are highlighted below.
Non-sexual crimes of violence
- Split Homicide etc. into two categories: Murder and culpable homicide, and Death by dangerous driving
- Reclassify Common assault as a crime, sitting as its own category within the Non-sexual crimes of violence group, which includes:
- 47001 Common Assault
- 47006 Minor assault of an emergency worker
- 47012 Common assault of a retail worker
- Reclassify Stalking (47009) as a crime, sitting within the Other non-sexual violence category of the Non-sexual crimes of violence group
- Move Female genital mutilation (11007) from Non-sexual crimes of violence – Other non-sexual violence to Non-sexual crimes of violence – Serious assault and attempted murder
Sexual crimes
- Split Other sexual crimes into five categories:
- Causing to view sexual activity or images
- Communicating indecently
- Threatening to or disclosing intimate images
- Indecent photos of children
- Other sexual crimes
Crimes of dishonesty
No changes
Damage and reckless behaviour
- Change the name from Fire-raising, vandalism etc. to Damage and reckless behaviour
- Split Vandalism etc. into two categories: Vandalism and Reckless conduct
Crimes against society
- Change name from Other crimes to Crimes against society
- Split Drug crimes into two categories: Drugs – possession and Drugs – supply
Coronavirus Restrictions
No changes
Offences
- Split the Miscellaneous offences group into two groups: Antisocial offences and Miscellaneous offences (multiple new categories)
- Remove Common assault and Stalking (reclassifying as Non-sexual crimes of violence) , which includes:
- 47001 Common Assault
- 47006 Minor assault of an emergency worker
- 47012 Common assault of a retail worker
- 47009 Stalking
- Change name from Motor vehicle offences to Road traffic offences
- Crime codes relating to the (mis)use of bikes moved from Miscellaneous offences to Road traffic offences
The codes affected are:
- 78/001 Dangerously riding a bicycle or tricycle
- 78/002 Carelessly or inconsiderately riding a bicycle or tricycle
- 78/003 Drunk when riding a bicycle
- 78/099 Bicycles, other offences
- 79/001 Pedestrian traffic offences
Protection of Workers Act
The Protection of Workers (Retail and Age-restricted Goods and Services) (Scotland) Act 2021 came into effect from 24 August 2021. The Act makes it an offence for a person to assault, threaten or abuse another person who is a retail worker and who is engaged, at the time of the offence, in retail work. Committing this offence while a retail worker is enforcing a statutory age restriction also constitutes an aggravation.
As a result the following new crime codes have been added to the Crime code list:-
Non-sexual crimes of violence
- 4003 - Serious Assault of a Retail Worker
- 47012 - Common Assault of a Retail Worker
Antisocial Offences
- 47013 - Threaten or Abuse Retail Worker
Breach of adult at risk banning order
From 1 April 2021, Adult Protection Act Offences (39/019) will no longer be counted as crimes. The reason for this is that the charge does not relate to a criminal offence and was created to allow the circumstances to be reported to the Procurator Fiscal. The Scottish Crime Recording Board reviewed the data recorded under this code and agreed not to back date this change as the numbers are negligible in the context of total recorded crime.
16.2.20 2022-23
Offensive Weapons Act
On 28th June 2022, Section 6 of the Offensive Weapons Act was implemented. This included the introduction of an offence of having a corrosive substance in a public place, including a new power of search for corrosive substances plus provisions in Part 3 (Sale and delivery of knives).
Part 4 of the legislation commenced on 27 March, 2023. This amends the definition of a flick knife to ensure that modern designs are also prohibited, and prohibits the possession in private of dangerous and offensive weapons to which Restriction of Offensive Weapons Act 1959 and Criminal Justice Act 1988 apply. The effect of Sections 44 and 46 is, coupled with existing law, to make it an offence as to the possession in any place of these weapons.
As a result the following new crime codes have been added to the Crime code list:-
Crimes against society
- 43/015 - Possession of a corrosive substance (Not used in crime)
- 43/016 - Possession of a corrosive substance (Used in other criminal activity)
- 43/017 - Possession of certain dangerous knives in a private place (Not used in crime)
- 43/018 - Possession of certain dangerous knives in a private place (Used in other criminal activity)
- 43/019 - Possession of prohibited offensive weapon in a private place (Not used in crime)
- 43/020 - Possession of prohibited offensive weapon in a private place (Used in other criminal activity)
16.3 Current Crime Code Classification
Crimes
Non-sexual crimes of violence
Murder and culpable homicide
- Murder
- Culpable homicide (Common Law)
- Corporate homicide
Death by dangerous driving
- Causing death by dangerous driving
- Death by careless driving when under influence of drink or drugs
- Causing death by careless driving
- Illegal driver involved in fatal accident
Serious assault and attempted murder
- Attempted murder
- Serious assault
- Causing injury etc. by Culpable & Reckless Conduct
- Illegal driver, disqualified/unlicensed etc. causing serious injury
- Serious assault of retail worker
- Female genital mutilation
Common assault
- Common Assault
- Minor assault of an emergency worker
- Common Assault of a Retail Worker
For the definition of Serious assault and the distinction between Serious assault and Common assault see SCRS manual
Robbery
- Robbery and assault with intent to rob
Domestic Abuse (Scotland) Act 2018
- Domestic Abuse of Male
- Domestic Abuse of Female
Other non-sexual violence
- Threats and extortion
- Cruelty (neglecting & cause) to and unnatural treatment of children
- Child Stealing (Plagium)
- Exposing child under 7 to risk of burning
- Abortion
- Concealment of pregnancy
- Possession of a firearm with intent to endanger life, commit crime etc.
- Abduction
- Ill treatment of mental patients
- Cruel and unnatural treatment of an adult
- Drugging
- Chemical weapon offences
- Forced Marriage
- Slavery or forced labour
- Human organ offences
- Offence of stalking
Sexual Crimes
Rape and attempted rape
- Rape
- Rape of male (16+)
- Rape of female (16+)
- Rape of older male child (13-15 years)
- Rape of older female child (13-15 years)
- Rape of young male child (Under 13)
- Rape of young female child (Under 13)
- Assault with intent to Rape
- Assault with intent to rape male (16+)
- Assault with intent to rape female (16+)
- Assault with intent to rape older male child (13-15)
- Assault with intent to rape older female child (13-15)
- Assault with intent to rape young male child (under 13)
- Assault with intent to rape young female child (under 13)
Sexual assault
- Sexual assault
- Sexual assault by penetration of male (16+)
- Sexual assault by penetration of female (16+)
- Sexual assault by penetration of male (13-15 years)
- Sexual assault by penetration of female (13-15 years)
- Sexual assault of male (16+)
- Sexual assault of female (16+)
- Sexual assault of older male child (13-15 years)
- Sexual assault of older female child (13-15 years)
- Sexual coercion of male (16+)
- Sexual coercion of female (16+)
- Sexual coercion of older male child (13-15 years)
- Sexual coercion of older female child (13-15 years)
- Assault by penetration of young male child (under 13)
- Assault by penetration of young female child (under 13)
- Sexual assault of young male child (under 13)
- Sexual assault of young female child (under 13)
- Cause young male child (under 13) to participate in sexual activity
- Cause young female child (under 13) to participate in sexual activity
- Sexual Intercourse with girl under 13
- Lewd and Libidinous practices
Causing to view sexual activity or images
- Coercing a person into being present/ looking at sexual activity
- Cause young child to be present/ look at sexual activity (under 13)
- Sexual exposure to a young child (under 13)
- Causing an older child (13-15) to be present/ look at sexual activity
- Sexual exposure older child (13-15)
- Public indecency
- Sexual exposure
Communicating indecently
- Communicating indecently
- Communicating indecently with young child (under 13)
- Communicate indecently older child (13-15)
Threatening to or disclosing an intimate image
- Threatening to disclose an intimate image
- Disclosure of an intimate image
Indecent photos of children
- Taking, distribution, possession etc of indecent photos of children
Crimes associated with prostitution
- Procuration (excluding homosexual acts)
- Brothel keeping
- Immoral traffic
- Offences related to prostitution
- Procuration of Homosexual Acts
- Soliciting services of person engaged in prostitution
Other sexual crimes
- Incest
- Illegal Homosexual Acts
- Attempt to commit unnatural crimes
- Voyeurism young child (under 13)
- Intercourse with older male child (13-15)
- Intercourse with older female child (13-15)
- Penetrative sexual activity with older male child (13-15)
- Penetrative sexual activity with older female child (13-15)
- Sexual activity with older male child (13-15)
- Sexual activity with older female child (13-15)
- Cause older male child (13-15) to participate in sexual activity
- Cause older female child (13-15) to participate in sexual activity
- Older male child (13-15) engaging in sexual conduct with another older child
- Older female child (13-15) engaging in sexual conduct with another older child
- Voyeurism older child (13-15)
- Communications Act 2003 (sexual)
- Voyeurism
- Sexual Intercourse with child under 16
- Carnal knowledge of mentally disordered person
- Householder permitting carnal knowledge of mentally disordered person
- Abducting girl under 18 woman mental disordered
- Person with custody & care of girl or other causing her seduction
- Clandestine Injury
- Conspiracy to commit sexual acts outside the U.K.
- Grooming of children for purposes of sexual offences
- Procuration of sexual services from child under 18
- Procuration of child under 18 for pornography
- Sexual abuse of trust of person under 18
- Sexual abuse of trust of mentally disordered person
- Bestiality
- Administering a substance for sexual purposes
- Possession of extreme pornography
Crimes of dishonesty
Housebreaking
- Theft by Housebreaking
- Housebreaking with intent to steal
- Attempted Housebreaking with intent to enter and steal
- Theft by Housebreaking domestic property (dwelling)
- Theft by Housebreaking domestic property (non-dwelling)
- Theft by Housebreaking other property
- Housebreaking with intent to steal domestic property (dwelling)
- Housebreaking with intent to steal domestic property (non-dwelling)
- Housebreaking with intent to steal other property
- Attempted Housebreaking with intent to enter and steal domestic property (dwelling)
- Attempted Housebreaking with intent to enter and steal domestic property (non-dwelling)
- Attempted Housebreaking with intent to enter and steal other property
Theft by opening lockfast places
- Theft by opening lockfast places (excluding motor vehicle)
- OLP (excluding motor vehicle) with intent to steal
- Attempted OLP (excluding motor vehicle) with intent to steal
Theft from a motor vehicle
- Theft by OLP from a motor vehicle
- OLP with intent to steal from a motor vehicle
- Attempted OLP with intent to steal from a motor vehicle
Theft of motor vehicle
- Theft of a motor vehicle and contents incl. taking and driving
- Attempted theft of a motor vehicle
Shoplifting
- Theft by shoplifting
Other theft
- Theft not elsewhere classified (excl motor vehicles)
- Theft of Pedal Cycle
- Theft from a motor vehicle not classified elsewhere
Fraud
- Fraud (including Statutory Fraud)
Other crimes of dishonesty
- Prevention of Crimes
- Vagrancy and known thief
- In building with intent to steal
- Reset
- Breach of Trust and Embezzlement
- Forgery and Uttering (excl currency off)
- Bankruptcy
- Clandestine removal of boats
- Clandestine removal of other property
- Corruption
- Currency Offences
- Insider dealing
- Proceeds of Crime
Damage and reckless behaviour
Fire-raising
- Fire-raising excluding Muirburn
- Fire-raising – Muirburn
Vandalism
- Computer Misuse Act 1990 - causing damage
- Vandalism
- Malicious Damage
Reckless Conduct
- Reckless conduct with firearms
- Flying aircraft to danger life or property
- Endangering rail passengers
- Reckless driving at common law
- Culpable neglect of duty
- Endangering ship by breach of duty
- Supply of glue sniffing kits
- Reckless Conduct (not with firearms)
- Culpable and reckless conduct involving aircraft
Crimes against society
Crimes against public justice
- Election etc. offences
- Public mischief (inc wasting police time)
- Falsely accusing (named) person of crime
- Escape and rescue (inc custody + prison)
- Resisting arrest
- Personation of police
- Failing to give name or remain with constable
- Obstructing constable in pursuance of duty
- General attempts to pervert course of justice
- Failure to notify police/provision of false information
- Protection of vulnerable groups
- Contempt of court
- Failing to appear after undertaking to police
- Publishing info re person < 16 on trial
- Not appearing for trial following bail
- Bail offences other than absconding/re-offending
- Accused failing to appear at trial diet
- Witness, offences by
- Prevarication on oath etc
- Perjury and subordination
- Breach of non harassment order (criminal court)
- Breach of non harassment order (civil court)
- Breach of anti social behaviour order
- Breach of sex offender order
- Breach of parenting order
- Breach of risk of sexual harm order (SHO) or interim risk of SHO
- Breach of football banning order
- Breach of violent offender order
- Breach of Domestic abuse interdict
- Breach of Forced Marriage Protection Order
- Breach of Trafficking & Exploitation Order
Weapons possession (not used)
- Possession of an offensive weapon
- Restriction of offensive weapon
- Having in a public place an article with a blade or point
- Having in a prison an article with a blade or point
- Possession of a firearm in a prison
- Possession of an offensive weapon (not elsewhere specified) in a prison
- Possession of an offensive weapon (not elsewhere specified) in a school
- Having in a school an article with a blade or point
- Possession of a Corrosive Substance
- Possession of certain dangerous knives in a private place
- Possession of prohibited offensive weapon in a private place
Weapons possession (used)
- Possession of an offensive weapon used in other criminal activity
- Having in a public place an article with a blade or point used in other criminal activity
- Possession of offensive weapon in a prison used in other criminal activity
- Having in a prison an article with a blade or point used in other criminal activity
- Possession of offensive weapon in a school used in other criminal activity
- Having in a school an article with a blade or point used in other criminal activity
- Possession of a Corrosive Substance used in other criminal activity
- Possession of certain dangerous knives in a private place used in other criminal activity
- Possession of prohibited offensive weapon in a private place used in other criminal activity
Drugs – Supply
- Illegal importation of drugs
- Production, manufacture or cultivation of drugs
- Supply, possession with intent to supply etc. of drugs
- Bringing drugs into prison
- Psychoactive Substance: Production, supply or possession in custody
- Psychoactive Substance: Other Offences
- Drugs, other offences
Drugs – Possession
- Possession of drugs
Other crimes against society
- Treason
- Sedition
- Official Secrets Act
- United Nations Sanctions Offences
- Protection of Cultural Property
- Mobbing and Rioting
- Public processions etc
- Trespass, crimes against public order
- Raves, crimes against public order
- Obstruct or hinder other emergency worker in pursuance of duty
- Terrorism - money laundering offences
- Prevention of Terrorism, other offences
- Explosive Substances Act 1883
- Unlawful use of explosives
- Reckless blasting
- Conspiracy
- Offences Relating to Serious Organised Crime
- Sacrilege
- Wrecking
- Piracy and Hijacking
Coronavirus restrictions crimes
Coronavirus restrictions
- Coronavirus restrictions
- Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Fail to provide info (SPR)
- Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Fail to provide info (£60)
- Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Fail to provide info (£120)
- Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Fail to provide info (£240)
- Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Fail to provide info (£480)
- Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Provide false/misleading info (SPR)
- Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Provide false/misleading info (£60)
- Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Provide false/misleading info (£120)
- Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Provide false/misleading info (£240)
- Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Provide false/misleading info (£480)
- Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Fail to quarantine (SPR)
- Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Fail to quarantine (£480)
- Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Contravene a requirement (SPR)
- Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Contravene a requirement (£480)
- Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Provide false/misleading passenger info (SPR)
- Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Provide false/misleading passenger info (£480)
- Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Obstruct (passenger info) (SPR)
- Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Obstruct (passenger info) (£60)
- Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Obstruct (passenger info) (£120)
- Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Obstruct (passenger info) (£240)
- Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Obstruct (passenger info) (£480)
- Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Obstruct (quarantining) (SPR)
- Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Obstruct (quarantining) (£480)
- Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Operator fail to provide passenger info
- Coronavirus HEPR Intl Travel - Testing offences
Offences
Antisocial offences
Threatening and abusive behaviour
- Breach of the peace
- Threatening or abusive behaviour
- Offensive behaviour at football (under the Offensive behaviour at football and threatening communication Scotland Act 2012)
- Threatening communications (under the Offensive behaviour at football and threatening communication Scotland Act 2012)
Racially aggravated conduct
- Racially aggravated harassment
- Racially aggravated conduct
Drunkenness and other conduct
- Drunk and incapable and habitual drunkenness
- Drunk in charge of a child
- Drunk and attempting to enter licensed premises
- Drunk or drinking in unlicensed premises
- Disorderly on licensed premises
- Drunk in or attempting to enter designated sports ground
- Refusing to quit licensed premises
- Consumption of alcohol in designated places, byelaws prohibited
- Antisocial behaviour offences
Urinating etc.
- Urinating etc.
Miscellaneous offences
Community and public order offences
- False or hoax calls to emergency services
- Bomb Hoaxes
- Children & young person offences (not elsewhere classified)
- Employment of children
- Education Acts
- Tattooing of Minors Act 1969
- Child Minding and Day Care for Children
- Employment of children (non-industrial)
- Employment of children (industrial)
- Selling loose cigarettes
- Not displaying notice cigarettes sold to 16 and over
- Selling cigarettes to persons under 16
- Offences against selling spray paint to children
- Smoking in car with child
- Handling obscene material
- Sex shop offences
- Social Security Offences
- Pedlars Act & Off Against Certificates Issued by Local Auth
- Licensing offences (Civic Govt (S) Act 1982)
- Obstruction of local official
- Common stairs offences
- Civic Government (S) Act 1982 (not elsewhere classified)
- Obstruction by pedestrian
- Touting
- Weights & Measures Acts
- Registration of Business Names
- Prices Act 1974
- Goods & Services (price control) Acts
- Counter Inflation Act 1973
- Patents Acts
- Copyright Acts
- Fair Trading Act 1973
- Restrictive Trade Practices Act 1976
- Consumer Protection Acts
- Consumer Credit Act 1974
- Trading offences
- Accommodation Agencies Act 1953
- Nursing Homes (Registration) (S) Act 1938
- Rent Acts
- Video Recordings Act 1984 (not elsewhere classified)
- Wireless Telegraphy Act 1949
- General post office/telecommunications offs
- Disclosure of information
- Interception of Communications Act 1984
- Data Protection Act 1984
- Computer Misuse Act 1990 - unauthorised access only
- Charitable collections offences
- Public utilities (gas electricity etc) legislation
- Supplementary benefits offences
- Sex Discrimination Act 1975
- Census Acts
- Race Relations Act
- Social work and community service offences
- Child Support Act 1991
Environmental offences
- Petroleum Acts
- Energy Acts
- Salmon and freshwater fisheries offences
- Sea fisheries offences
- Factories legislation (not elsewhere classified)
- Fire Precautions Acts
- Health and Safety at Work Acts
- Employment and property protection legislation
- Employment Protection (Consolidation) Act 1978
- Wages Councils Act 1979
- Trade Union & Labour Relations Act 1974
- Mines Acts
- Shops Acts
- Merchant Shipping Acts (not elsewhere classified)
- Parks etc
- Litter Offences
- Refuse Disposal (Amenity) Act 1978
- Oil pollution in navigable waters
- Control of pollution
- Clean air Acts
- Sanitary laws
- Food Safety Act 1990
- Milk Acts
- Control of Food Premises Act 1977
- Water (S) Acts
- Town and country planning acts
- Prevention of Damage by Pests Act 1949
- Housing (S) Acts
- Caravan Sites & Control of Development Act 1960
- Methylated Spirits (Sale by Retail) (S) Act 1937
- Therapeutic Substances Act 1956
- Cinematograph Acts
- Other Environmental Offences
- Contravention of section 6(1) by continuing to operate proscribed process
- Failure to comply with or contravention of enforcement or prohibition notice
- Other conservation offences
- Offences relating to road works
- Lighting fires without consent of owner
- Lodging without consent of owner
- Agricultural offences
- Building legislation
- Aviation legislation
- Archaeological legislation
Licensing offences
- Betting
- Gaming
- Gaming by means of machines
- Lotteries and amusements with prizes
- Brokers (Licensed) and Auction Acts
- Crossbow Offences
- Firearms, Miscellaneous Offences
- Air weapons licensing offences
- Sale of drink to person under 18
- Employing a person under 18 in a bar
- Licensed person, employee or agent drunk in licensed premise
- Permitting riotous behaviour in licensed premises
- Permitting betting and gaming offences in licensed premises
- Contravening condition of premises with children's certificate
- Dealing wholesale other than from permitted premises
- Wholesaler selling liquor to person under 18
- Wholesaler permitting person under 18 to sell alcohol
- License holder of off sales permit person under 18 to sell alcohol
- Licensed persons, other offences
- Carriage of liquor in contract carriage
- Consuming outwith permitted hours
- Trafficking without a licence
- Club licensing offences
- Hawking excisable liquor
- Person under 18 buying excisable liquor or consuming in bar
- Consuming liquor on licensed premises on credit (other than hotels)
- Inducing holder of off-sales license to sell liquor illegally
- Purchasing excise liquor for consumption by person under 18
- Breaking sales restrictions on licences other than for pubs
- Alcohol offences, travelling to and from sporting event
- Sports ground offences (possessing alcohol etc)
- Confiscation of alcohol from person under 18
- Liquor licensing laws, other offences
- Pawnbrokers, Firearms Offences
- Hackney carriages offences
- Public service vehicles offences
Wildlife offences
- Cruelty to animals (ex dogs) inc killing and maiming cattle
- Rabies Orders
- Animals, offences involving (ex dogs, birds elsewhere classified)
- Birds, offences involving
- Pet and kept animals
- Cruelty to dogs
- Protection of livestock from dogs
- Guard Dogs Act 1975
- Dogs bred for fighting
- Keeping dogs under prop control, contravention of an order
- Hunting with dogs
- Cruelty to wild animals
- Offences involving badgers
- Other wildlife offences
- Dogs, other offences
- Possession of salmon or trout unlawfully obtained
- Possession of salmon or trout as result of offence
- Poaching and game laws
- Deer (S) Offences
Other misc. offences
- Aliens and Immigration Offences
- Offences relating to persons disqualified from working with children
- Prevent a person feeding a baby milk in a public place
- Keeping and Supply of Explosives
- Harbour Acts
- Absentees and deserters
- Naval military and air force, other offences
- Dog Fouling
- Smoking in public places
- Medical Acts
- Dentists Acts
- Nurses (S) Acts
- Opticians Acts
- Venereal Diseases Act 1917
- Poisons Act
- Medicines Acts
- National Health Service (S) Acts
- Railways
- Bigamy
- False declarations
- Births deaths marriages, registration offences
- Marriage (S) Act 1977
- Revenue and excise Offences (excluding Vehicle and Drugs)
- Prisons (S) Act 1989 (not elsewhere classified)
- Investment legislation
- Industrial training and statistics of trade offences
- Building Societies Act 1986
- Fire services legislation
- Emergency powers Acts
- Solicitors (S) Acts
- Local Government legislation
- Architects registration offences
- Estate Agents Acts
- Insurance Brokers (Registration) Act 1977
- Legal Aid and advice legislation
- Adoption (S) Act 1978
- Theatres Act 1968
- Industrial and provident societies offences
- Friendly Societies Acts
- Credit Union Acts 1979
- Lands Valuation (S) Act
- Scotland Act offences
- Ethical Standards in Public Life
- Pensions Acts
- Antisocial behaviour, landlord offences
- Offences under the Charities and Trustees Inv Act
- Failure to comply with a Property Factor Enforcement Order (PFEO)
Road traffic offences
Dangerous and careless driving
- Dangerous driving offences
- Driving carelessly
Driving under the influence
- Driving motor vehicle while unfit through drink or drugs
- In charge of motor vehicle while unfit through drink/drugs
- Driving motor vehicle with blood alcohol content above prescribed limit
- In charge of motor vehicle while blood alcohol content above limit
- Failure to provide breath specimen at roadside
- Failure to provide breath, blood or urine specimen at police station
- Driving motor vehicle while under influence of controlled drug above prescribed limit
- In charge of motor vehicle while under influence of controlled drug above prescribed limit
Speeding
- Speeding in Restricted Areas
- Other Speeding Offences
Unlawful use of motor vehicle
- Vehicle excise License Offences
- Using Motor Vehicle Without Test Certificate
- Driving While Disqualified from Holding or Obtaining Licence
- Driving Without a Licence (including under age)
- Driving Licence, Other Offences
- Failure to Insure Against Third Party Risks
- Insure Against Third Party Risks, Other Offences
- Registration or Identification Mark Offences (Not Lighting)
Vehicle defect offences
- Lighting Offences, Motor Vehicle
- Construction & Use Regulations (Other Than Lighting
Seat Belt Offences
- Seat Belt Offences
Mobile Phone Offences
- Mobile Phone Offences
Other road traffic offences
- Dangerously riding a bicycle or tricycle
- Carelessly or inconsiderately riding a bicycle or tricycle
- Drunk when riding a bicycle
- Bicycles, other offences
- Pedestrian traffic offences
- Driver's Neglect of Traffic Directions (Not Pedestrian Crossing)
- Driver's contravention of Pedestrian Crossing Regulations
- Accident Offences
- Parking Offences
- Failing to Provide Info to Identify Driver of Motor Vehicle
- Motorway Traffic Offences
- Clearway Offences
- Motor Vehicle Records of Work (eg Tachograph) Offences
- Motor Vehicle, Other Offences
Contact
Email: justice_analysts@gov.scot
There is a problem
Thanks for your feedback